Learn how to configure security settings for Managed DevOps Pools. There are two ways to configure security settings:
- When you create a pool by using the Security tab
- After you create a pool by using the Security settings pane
By default, pools that you create with Managed DevOps Pools are configured for all projects in a single organization. You can optionally limit access to specific projects in the organization, and you can also grant access to other organizations.
If you configure your pool and grant access to all projects, the pool is added to the projects for which you have the appropriate permissions. If you configure your pool and grant access to specific projects, you must have permission to add the pool in all of the designated projects, or the pool creation fails.
To see the permissions required to configure Managed DevOps Pools in your organization and projects, see Prerequisites: Verify Azure DevOps permissions.
Use a pool with a single organization
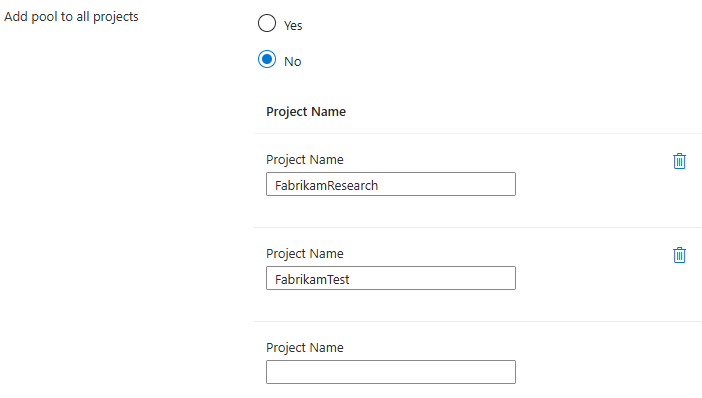
By default, Managed DevOps Pools is configured with a single Azure DevOps organization that you specify when you create the pool. When your pool is configured for a single organization, the organization name is displayed and configured in Pool settings.
By default, the Add pool to all projects setting is set to Yes, and access to the Managed DevOps Pool is granted to all projects in the organization. To limit which projects in your organization can use the pool, select No, and then specify which projects should have access.
You can configure organizations in the organizationProfile property of the Managed DevOps Pools resource.
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"resources": [
{
"name": "fabrikam-managed-pool",
"type": "microsoft.devopsinfrastructure/pools",
"apiVersion": "2025-01-21",
"location": "eastus",
"properties": {
...
"organizationProfile": {
"organizations": [
{
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-tailspin",
"projects": [],
"parallelism": 4
}
],
"permissionProfile": {
"kind": "CreatorOnly"
},
"kind": "AzureDevOps"
}
}
]
}
The organizationProfile section has the following properties.
| Property |
Description |
organizations |
A list of the organizations that can use your pool. The url property specifies the URL of the organization. The projects property is a list of project names that can use the pool (an empty list supports all projects in the organization). The parallelism property specifies the number of agents that the organization can use. The sum of the parallelism for the organizations must match the maximum agents setting for the pool. |
permissionProfile |
This value specifies the permission you grant to the Azure DevOps pool when you create it. You can set this value only when you create a pool. Allowed values are Inherit, CreatorOnly, and SpecificAccounts. If you specify specificAccounts, provide a single email address or a list of email addresses for the users property. Otherwise, omit users. For more information, see Pool administration permissions. |
kind |
This value specifies the type of organization for the pool, and must be set to Azure DevOps. |
You can configure organizations in the organization-profile parameter when you create or update a pool.
az mdp pool create \
--organization-profile organization-profile.json
# other parameters omitted for space
The following example shows an organization-profile object that's configured for all projects in the fabrikam-tailspin organization with the parallelism value set to 1.
{
"AzureDevOps":
{
"organizations": [
{
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-tailspin",
"projects": [],
"parallelism": 1
}
]
}
}
The organizationProfile section has the following properties.
| Property |
Description |
AzureDevOps |
This value is the name of the object defined in organization-profile and must be set to Azure DevOps. |
organizations |
A list of the organizations that can use your pool. openAccess specifies whether Managed DevOps Pools configures open access for the pool during pool creation. The url property specifies the URL of the organization. The projects property is a list of project names that can use the pool (an empty list supports all projects in the organization). The parallelism property specifies the number of agents that this organization can use. The sum of the parallelism for the organizations must match the maximum agents setting for the pool. |
permissionProfile |
This property specifies the permission you grant to the Azure DevOps pool when you create it. You can set this value only when you create a pool. Allowed values are Inherit, CreatorOnly, and SpecificAccounts. If you specify specificAccounts, provide a single email address or a list of email addresses for the users property. Otherwise, omit users. For more information, see Pool administration permissions. |
You can configure organizations in the organizationProfile property of the Managed DevOps Pools resource.
resource managedDevOpsPools 'Microsoft.DevOpsInfrastructure/pools@2025-01-21' = {
name: 'fabrikam-managed-pool'
location: 'eastus'
properties: {
organizationProfile: {
organizations: [
{
url: 'https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-tailspin'
projects: []
parallelism: 4
}
]
permissionProfile: {
kind: 'CreatorOnly'
}
kind: 'AzureDevOps'
}
}
}
The organizationProfile section has the following properties.
| Property |
Description |
organizations |
A list of the organizations that can use your pool. The url property specifies the URL of the organization. The projects property is a list of project names that can use the pool (an empty list supports all projects in the organization). The parallelism property specifies the number of agents that this organization can use. The sum of the parallelism for the organizations must match the maximum agents setting for the pool. |
permissionProfile |
This property specifies the permission you grant to the Azure DevOps pool when you create it. You can set this value only when you create a pool. Allowed values are Inherit, CreatorOnly, and SpecificAccounts. If specificAccounts is specified, provide a single email address or a list of email addresses for the users property. Otherwise, omit users. For more information, see Pool administration permissions. |
kind |
This value specifies the type of organization for the pool, and must be set to Azure DevOps. |
Use a pool in multiple organizations
To use your pool with multiple Azure DevOps organizations, enable Use pool in multiple organizations. For each organization, specify the projects that are permitted to use the pool, or leave this field blank to allow all projects. Configure the Parallelism for each organization by specifying what portions of the concurrency, as specified by Maximum agents value for the pool, to allocate to each organization. The sum of the parallelism for all organizations must equal the maximum concurrency of the pool. For example, if Maximum agents is set to five, the sum of the parallelism for the specified organizations must be five. If the Maximum agents value is set to one, you can use the pool with only one organization.
In the following example, the pool is configured to be available for the FabrikamResearch and FabrikamTest projects in the fabrikam-tailspin organization, and to all projects in the fabrikam-blue organization.
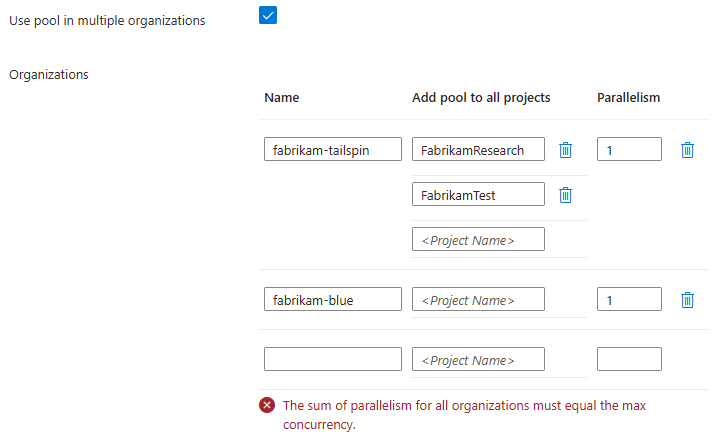
If you receive an error like The sum of parallelism for all organizations must equal the max concurrency, ensure that the Maximum agents count for the pool matches the sum of the Parallelism column.
To configure your pool so that multiple organizations can use it, add more organizations to the organizations list. The following example has two organizations configured. The first organization is configured to use Managed DevOps Pools for all projects, and the second organization can use it with only two projects. In this example, the maximum agents setting for the pool is four, and each organization can use two of these four agents.
"organizationProfile": {
"organizations": [
{
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-tailspin",
"projects": [],
"parallelism": 2
},
{
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-prime",
"projects": [ "fabrikam-dev", "fabrikam-test" ],
"parallelism": 2
}
],
"permissionProfile": {
"kind": "CreatorOnly"
},
"kind": "AzureDevOps"
}
You can configure organizations in the organization-profile parameter when you create or update a pool.
az mdp pool create \
--organization-profile organization-profile.json
# other parameters omitted for space
To configure your pool so that multiple organizations can use it, add more organizations to the organizations list. The following example has two organizations configured. The first organization is configured to use Managed DevOps Pools for all projects, and the second organization can use it with only two projects. In this example, the maximum agents setting for the pool is four, and each organization can use two of these four agents.
{
"AzureDevOps":
{
"organizations": [
{
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-tailspin",
"projects": [],
"parallelism": 2
},
{
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-prime",
"projects": [ "fabrikam-dev", "fabrikam-test" ],
"parallelism": 2
}
]
}
}
To configure your pool so that multiple organizations can use it, add more organizations to the organizations list. The following example has two organizations configured. The first organization is configured to use Managed DevOps Pools for all projects, and the second organization can use it with only two projects. In this example, the maximum agents setting for the pool is four, and each organization can use two of these four agents.
organizationProfile: {
organizations: [
{
url: 'https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-tailspin'
projects: []
parallelism: 2
}
{
url: 'https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-prime'
projects: ['fabrikam-dev', 'fabrikam-test']
parallelism: 2
}
]
permissionProfile: {
kind: 'CreatorOnly'
}
kind: 'AzureDevOps'
}
To configure open access for pipelines, you must have the following permissions in addition to the permissions described in Prerequisites - Verify Azure DevOps permissions:
By default, you must explicitly authorize each pipeline definition to run in a self-hosted agent pool (like a pool created by using Managed DevOps Pools) before it runs for the first time in that pool.
Azure DevOps provides the following modes to authorize pipelines to run in an agent pool.
- Authorize specific pipelines (default): Individually authorize specific pipelines from an Azure DevOps project to run in the pool.
- Open access: Configure an agent pool at the project level to be available for all pipelines in that project.
Enable Allow all pipelines to run on the pool without an approval (open access) to configure the Open access agent pool setting in Azure DevOps when you create the pool.
You can configure the Allow all pipelines to run on the pool without an approval (open access) setting in Managed DevOps Pools only when you create the pool. After the pool is created, you can view and configure Open access on the corresponding agent pool in Azure DevOps for each project that uses the pool.
To configure access to the pool from all pipelines in the designated projects, enable Allow all pipelines to run on the pool without an approval (open access).
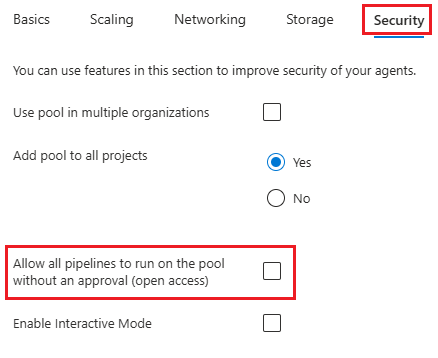
- If Add pool to all projects is set to Yes, Managed DevOps Pools configures Open access for all pipelines in all projects.
- If Add pool to all projects is set to No, Managed DevOps Pools configures Open access for all pipelines in only the listed projects.
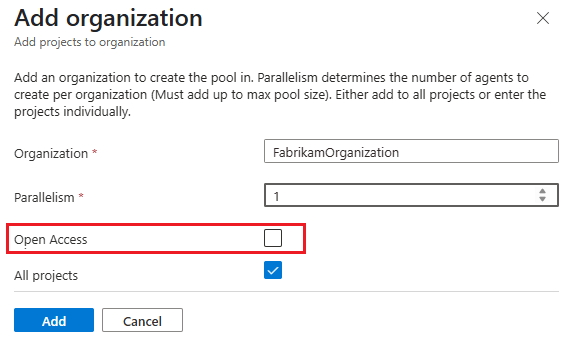
If you enable Use pool in multiple organizations, you can specify Open access individually for each organization.
Note
The Open access setting is present when you use api-version 2025-01-21 and higher.
You can configure organizations in the organizationProfile property of the Managed DevOps Pools resource. The following example has two organizations configured:
- The
fabrikam-tailspin organization is configured with Open access on all projects.
- The
fabrikam-prime organization is configured for availability with two projects, with Open access enabled only on these two projects.
"organizationProfile": {
"organizations": [
{
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-tailspin",
"projects": [],
"openAccess": true,
"parallelism": 2
},
{
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-prime",
"projects": [ "fabrikam-dev", "fabrikam-test" ],
"openAccess": true,
"parallelism": 2
}
],
"permissionProfile": {
"kind": "CreatorOnly"
},
"kind": "AzureDevOps"
}
You can configure Open access only when you create a pool. To change the Open access setting after you create a pool (including adding or removing projects from your Managed DevOps Pools configuration), you must manually configure Open access on the corresponding agent pool in Azure DevOps for each project that uses the pool.
You can configure the openAccess setting in the organization-profile parameter when you create a pool.
az mdp pool create \
--organization-profile organization-profile.json
# other parameters omitted for space
The following orgaization-profile example has two organizations configured:
- The
fabrikam-tailspin organization is configured with Open access on all projects.
- The
fabrikam-prime organization is configured for availability with two projects, with Open access enabled only on these two projects.
{
"AzureDevOps":
{
"organizations": [
{
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-tailspin",
"projects": [],
"parallelism": 2
},
{
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-prime",
"projects": [ "fabrikam-dev", "fabrikam-test" ],
"parallelism": 2
}
]
}
}
You can configure Open access only when you create a pool. To change the Open access setting after you create a pool (including adding or removing projects from your Managed DevOps Pools configuration), you must manually configure Open access on the corresponding agent pool in Azure DevOps for each project that uses the pool.
Note
The Open access setting is present when using api-version 2025-01-21 and higher.
You can configure organizations in the organizationProfile property of the Managed DevOps Pools resource. The following example has two organizations configured:
- The
fabrikam-tailspin organization is configured with Open access on all projects.
- The
fabrikam-prime organization is configured for availability with two projects, with Open access enabled only on these two projects.
organizationProfile: {
organizations: [
{
url: 'https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-tailspin'
projects: []
openAccess: true
parallelism: 2
}
{
url: 'https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam-prime'
projects: ['fabrikam-dev', 'fabrikam-test']
openAccess: true
parallelism: 2
}
]
permissionProfile: {
kind: 'CreatorOnly'
}
kind: 'AzureDevOps'
}
You can configure Open access only when you create a pool. To change the Open access setting after you create a pool (including adding or removing projects from your Managed DevOps Pools configuration), you must manually configure Open access on the corresponding agent pool in Azure DevOps for each project that uses the pool.
If you try to run a pipeline that isn't authorized to access your agent pool, you receive an error like "This pipeline needs permission to access a resource before this run can continue." You can resolve this issue by configuring open access, as described in the previous section, or by explicitly authorizing the pipeline to run in the agent pool.
If your tests need an interactive login for UI testing, enable interactive login by enabling the EnableInteractiveMode setting.
You can configure interactive mode in the osProfile section of the fabricProfile property. Set logonType to Interactive to enable interactive mode, or Service to disable interactive mode.
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"resources": [
{
"name": "fabrikam-managed-pool",
"type": "microsoft.devopsinfrastructure/pools",
"apiVersion": "2025-01-21",
"location": "eastus",
"properties": {
...
"fabricProfile": {
"sku": {...},
"images": [...],
"osProfile": {
"secretsManagementSettings": {...},
"logonType": "Interactive"
},
"storageProfile": {...},
"kind": "Vmss"
}
}
]
}
You can configure interactive mode by using the logonType property in the osProfile section in the fabric-profile parameter when you create or update a pool.
az mdp pool create \
--fabric-profile fabric-profile.json
# other parameters omitted for space
The following example shows the osProfile section of the fabric-profile.json file with Interactive mode enabled.
{
"vmss": {
"sku": {...},
"images": [...],
"osProfile": {
"secretsManagementSettings": {...},
"logonType": "Interactive"
},
"storageProfile": {...}
}
}
Interactive mode is configured in the osProfile section of the fabricProfile property. Set logonType to Interactive to enable interactive mode, or Service to disable interactive mode.
resource managedDevOpsPools 'Microsoft.DevOpsInfrastructure/pools@2025-01-21' = {
name: 'fabrikam-managed-pool'
location: 'eastus'
properties: {
fabricProfile: {
sku: {...}
images: [...]
osProfile: {
secretsManagementSettings: {...}
logonType: 'Interactive'
}
storageProfile: {...}
kind: 'Vmss'
}
}
}
As part of the Managed DevOps Pool creation process, an agent pool is created at the Azure DevOps organization level, and a project level agent pool is created in each designated project. The Pool administration permissions setting specifies which users are granted the administrator permission on the newly created agent pools in Azure DevOps. To view and manage the Azure DevOps agent pool permissions after the Managed DevOps Pool is created, see Create and manage agent pools: Security of agent pools.
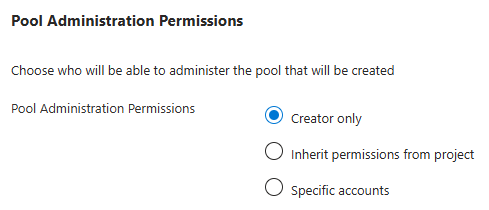
- Creator only: This setting adds the user who created the Managed DevOps Pool as an administrator of the Azure DevOps agent pool, and sets Inheritance to Off in the agent pool security settings. Creator only is the default setting.
- Inherit permissions from project: This setting adds the user who created the Managed DevOps Pool as an administrator of the Azure DevOps agent pool, and sets Inheritance to On in the agent pool security settings.
- Specific accounts: You can use this setting to specify the accounts that you want to add as administrators of the agent pool in Azure DevOps. By default, the pool creator is included.
You can configure the Pool administration permissions setting on the Security tab when you create the pool. It isn't displayed in the Security settings after the pool is created. To view and manage the Azure DevOps agent pool permissions after you create the pool, see Create and manage agent pools - Security of agent pools.
You can configure pool administration permissions in the permissionsProfile property of the organizationProfile section of the Managed DevOps Pools resource.
{
"organizationProfile": {
"organizations": [...],
"permissionProfile": {
"kind": "CreatorOnly"
},
"kind": "AzureDevOps"
}
You can set the permissionProfile property only when you create the pool. Allowed values are Inherit, CreatorOnly, and SpecificAccounts.
CreatorOnly: This setting adds the user who created the Managed DevOps Pool as an administrator of the Azure DevOps agent pool, and sets Inheritance to Off in the agent pool security settings. Creator only is the default setting.Inherit: This setting adds the user who created the Managed DevOps Pool as an administrator of the Azure DevOps agent pool, and sets Inheritance to On in the agent pool security settings.SpecificAccounts: You can use this setting to specify the accounts that you want to add as administrators of the agent pool in Azure DevOps. By default, the pool creator is included.
"organizationProfile": {
"organizations": [...],
"permissionProfile": {
"kind": "SpecificAccounts",
"users" : ["[email protected]", "[email protected]" ]
},
"kind": "AzureDevOps"
}
You can configure pool administration permissions in the organization-profile parameter when you create a pool.
az mdp pool create \
--organization-profile organization-profile.json
# other parameters omitted for space
{
"AzureDevOps":
{
"organizations": [...],
"permissionProfile": {
"kind": "CreatorOnly"
}
}
}
You can set the permissionProfile property only when you create the pool. Allowed values are Inherit, CreatorOnly, and SpecificAccounts.
CreatorOnly: This setting adds the user who created the Managed DevOps Pool as an administrator of the Azure DevOps agent pool, and sets Inheritance to Off in the agent pool security settings. Creator only is the default setting.Inherit: This setting adds the user who created the Managed DevOps Pool as an administrator of the Azure DevOps agent pool, and sets Inheritance to On in the agent pool security settings.SpecificAccounts: You can use this setting to specify the accounts that you want to add as administrators of the agent pool in Azure DevOps. By default, the pool creator is included. Provide a single email address or a list of email addresses for the users property. Otherwise, omit users.
{
"AzureDevOps" : {
"organizationProfile": {
"organizations": [...],
"permissionProfile": {
"kind": "SpecificAccounts",
"users" : ["[email protected]", "[email protected]" ]
}
}
}
}
You can configure pool administration permissions in the permissionsProfile property of the organizationProfile section of the Managed DevOps Pools resource.
organizationProfile: {
organizations: [...]
permissionProfile: {
kind: 'CreatorOnly'
}
kind: 'AzureDevOps'
}
You can set the permissionProfile property only when you create the pool. Allowed values are Inherit, CreatorOnly, and SpecificAccounts.
CreatorOnly: This setting adds the user who created the Managed DevOps Pool as an administrator of the Azure DevOps agent pool, and sets Inheritance to Off in the agent pool security settings. Creator only is the default setting.Inherit: This setting adds the user who created the Managed DevOps Pool as an administrator of the Azure DevOps agent pool, and sets Inheritance to On in the agent pool security settings.SpecificAccounts: You can use this setting to specify the accounts that you want to add as administrators of the agent pool in Azure DevOps. By default, the pool creator is included. Provide a single email address or a list of email addresses for the users property. Otherwise, omit users.
organizationProfile: {
organizations: [...]
permissionProfile: {
kind: 'SpecificAccounts'
users: ['[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
kind: 'AzureDevOps'
}
Managed DevOps Pools offers the ability to fetch certificates from an Azure key vault during provisioning. The certificates already exist on the machine by the time it runs your pipelines.
To use this feature, you must:
Configure an identity on your pool. You must give this identity Key Vault Secrets User permission to fetch the secret from your key vault. To assign your identity to the Key Vault Secrets User role, see Provide access to key vault keys, certificates, and secrets with an Azure role-based access control.
The principal that configures key vault integration settings (your account if you're configuring key vault settings) must have the Key Vault Certificate User role assignment on the key vault where the certificates are stored.
To enforce network isolation for your Azure Key Vault instance to only permit authorized resources access, you must add the following IP addresses to your Azure Key Vault allow list. The following IP address ranges are in an Azure service tag named DevOpsInfrastructure.
| Location |
IP address range |
| australiaeast |
4.198.194.192/28 |
| brazilsouth |
74.163.143.32/28 |
| canadacentral |
130.107.66.0/28 |
| centralindia |
98.70.255.112/28 |
| centralus |
72.152.33.16/28 |
| eastus2 |
72.153.21.192/28 |
| germanywestcentral |
131.189.121.128/28 |
| northeurope |
72.145.24.48/28 |
| southeastasia |
135.171.33.48/28 |
| switzerlandnorth |
74.161.82.192/28 |
| uksouth |
131.145.107.64/28 |
| westus3 |
57.154.125.208/28 |
Note
As of api-version 2025-01-21, if you use this feature, you can use only a single identity on the pool.
You can use only one identity to fetch secrets from the key vault.
You set Managed DevOps Pools certificate settings at the pool level, and some of the settings are specific for Windows or Linux. If your workflow requires both Linux and Windows images, you might have to divide them into multiple pools if you can't find a common set of certificate settings that work for both Windows and Linux.
The following settings configure the certificates fetched from your key vault:
- Certificates (
observedCertificates): This setting specifies the certificates to be fetched from your key vault and installed on all machines in your pool.
- Certificate store location (
certificateStoreLocation): This setting specifies the location to install the certificates on your agent.
- Windows agents: Specify
LocalMachine or CurrentUser.
- Linux agents: The setting Certificate store location is only supported on Ubuntu distributions. Specify the disk path to store the certificates (for example,
/var/lib/waagent/Microsoft.Azure.KeyVault/app1).
For Ubuntu distributions, if you specify the trusted store location (for example, /usr/local/share/ca-certificates), the certificate is added to that certificate store as root. For more information, see Install a root CA certificate in the trust store.
- Certificate store name (
certificateStoreName)
- Windows agents: This setting specifies the name of the certificate store. It's either
My (local certificate store, which is the default if no name is specified) or Root (trusted root location).
- Linux agents: This setting isn't used on Linux agents.
- Exportable private keys (
keyExportable): This setting specifies whether the key of the certificates is exportable. The default is false.
You can configure key vault integration in Settings > Security.
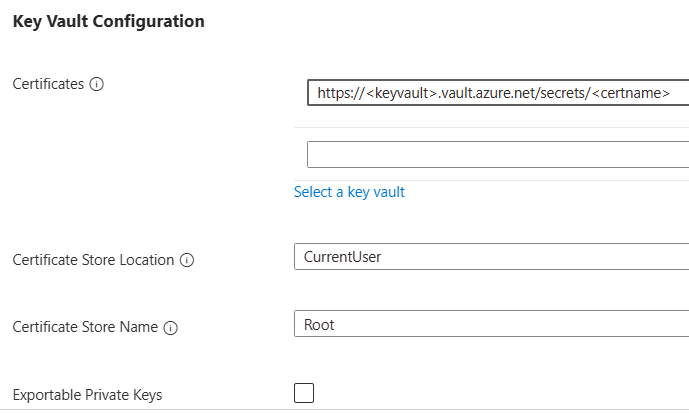
You can configure key vault integration settings only after you create the pool. You can't configure key vault integration settings when you create the pool. They're not displayed on the Security tab during pool creation.
You can configure Azure Key Vault in the osProfile section of the fabricProfile property. Set secretManagementSettings to be able to access the desired certificate.
Note
The osProfile.certificateStoreName property is available only in apiVersion 2025-01-21 and later.
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"resources": [
{
"name": "fabrikam-managed-pool",
"type": "microsoft.devopsinfrastructure/pools",
"apiVersion": "2025-01-21",
"location": "eastus",
"properties": {
...
"fabricProfile": {
"sku": {...},
"images": [...],
"osProfile": {
"secretsManagementSettings": {
"certificateStoreLocation": "LocalMachine",
"certificateStoreName": "Root",
"observedCertificates": [
"https://<keyvault-uri>/secrets/<certificate-name>"
],
"keyExportable": false
}
},
"storageProfile": {...},
"kind": "Vmss"
}
}
]
}
You can configure Azure Key Vault in the osProfile section of the fabricProfile property when you create or update a pool. Set the secretManagementSettings to be able to access the desired certificate.
az mdp pool create \
--fabric-profile fabric-profile.json
# other parameters omitted for space
The following example shows the osProfile section of the fabric-profile.json file with secretsManagementSettings configured.
{
"vmss": {
"sku": {...},
"images": [...],
"osProfile": {
"secretsManagementSettings": {
"certificateStoreLocation": "LocalMachine",
"observedCertificates": [
"https://<keyvault-uri>/secrets/<certificate-name>"
],
"keyExportable": false
},
"logonType": "Interactive"
},
"storageProfile": {...}
}
}
You can configure Azure Key Vault in the osProfile section of the fabricProfile property. Set secretManagementSettings to be able to access the desired certificate.
Note
The osProfile.certificateStoreName property is available only in apiVersion 2025-01-21 and later.
resource managedDevOpsPools 'Microsoft.DevOpsInfrastructure/pools@2025-01-21' = {
name: 'fabrikam-managed-pool'
location: 'eastus'
properties: {
fabricProfile: {
sku: {...}
images: [...]
osProfile: {
secretsManagementSettings: {
certificateStoreLocation: 'LocalMachine'
certificateStoreName: 'Root'
observedCertificates: 'https://<keyvault-uri>/secrets/<certificate-name>'
keyExportable: false
}
}
kind: 'Vmss'
}
}
}
Certificates that are retrieved by using the SecretManagementSettings on your pool automatically sync with the most recent versions published within the key vault. These secrets are on the machine by the time it runs its first pipeline, meaning you can save time and remove tasks for fetching certificates.
Important
Provisioning of your agent virtual machines fails if the secret can't be fetched from the key vault due to a permissions or network issue.
For Windows, you can set the Certificate Store Location value to LocalMachine or CurrentUser. This setting ensures that the secret is installed at that location on the machine. For specific behavior of how secret retrieval works, see Azure Key Vault extension for Windows.
For Linux, you can set the Certificate Store Location value to any directory on the machine, and the certificates are downloaded and synced to that location. For specifics on default settings and secret behavior, see Azure Key Vault virtual machine extension for Linux.
Related content






