Learn the answers to common questions, patterns, and best practices for Azure Cache for Redis.
Redis licensing change
What are the changes have been made to Redis licensing?
The Redis open-source project has changed to a dual-license model with support for the Redis Source Available License version 2 (RSALv2) or Server-Side Public License version 1 (SSPLv1). Refer to the Redis press release for more information. Also see the Microsoft blog post on the Redis licensing change.
Is Azure Cache for Redis now also covered by the RSALv2 and SSPLv1 licenses?
No, Azure Cache for Redis is offered to customers under the Microsoft terms of service. The RSALv2 and SSPLv1 licenses do not apply to your use of Azure Cache for Redis.
Will my Azure Cache for Redis instance continue to receive patches and bug fixes?
Yes, Azure Cache for Redis, Azure Cache for Redis Enterprise, and Enterprise Flash will continue to receive patches and bug fixes even after the licensing announcement.
What do I need to do as an Azure Cache for Redis customer in response to this licensing announcement?
There is no action required for our Azure customers regarding the licensing announcement.
Deprecated Services
Which Azure Cache for Redis services were deprecated?
Managed Cache service -Managed Cache service was retired November 30, 2016.
In-Role Cache - In-Role Cache was retired November 30, 2016.
Caches with a dependency on Cloud Services (classic)
What should I do with any instances of Azure Cache for Redis that depend on Cloud Services (classic)?
You should migrate all caches with a dependency on Cloud Services (classic). In August 2021, we announced Cloud Services (classic) will be retired on August 31, 2024. Any instances of Azure Cache for Redis that are dependent on Cloud Services (classic) need to be retired by the same date.
You should migrate caches with a dependency on Cloud Services (classic) before August 31, 2024.
How many caches are affected?
We’ve made an effort to migrate as many caches as transparently possible. Because of this, few caches and customers are affected.
How do I know if a cache is affected?
Check Azure Advisor Recommendations. If your cache is affected, you see a recommendation in your subscription.
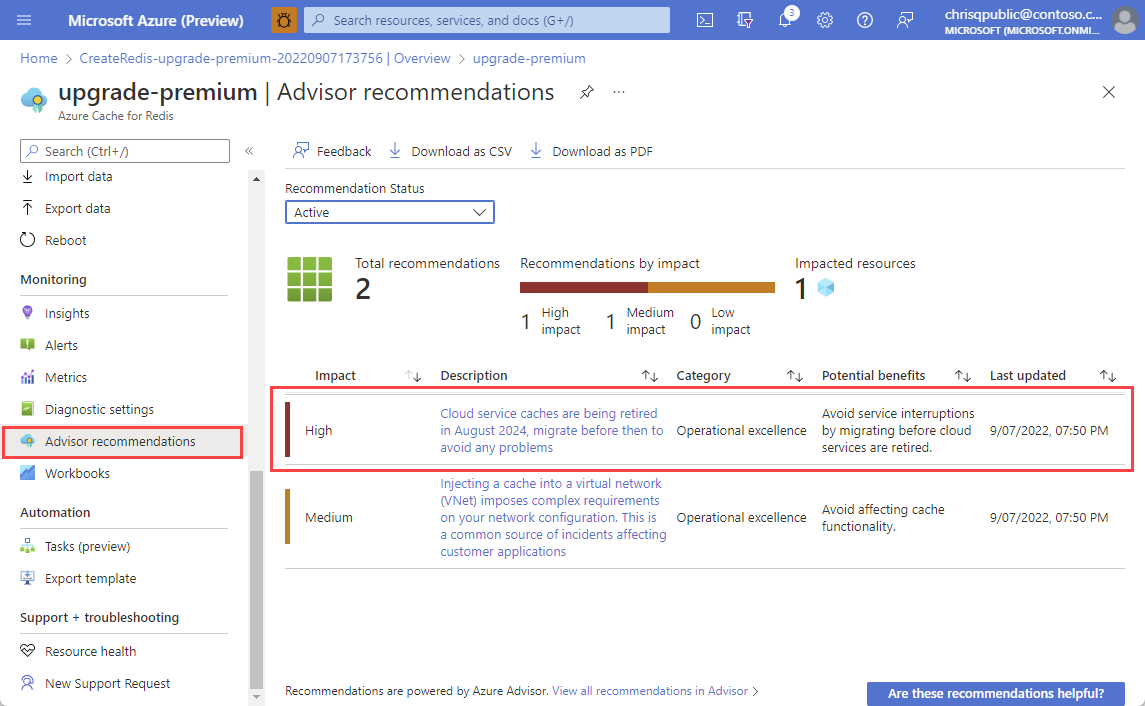
How do I migrate Cloud Services (classic) caches to Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets?
We have migrated most caches from being built on Cloud Services (classic) to being built on Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets. Migrating to Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets removes the dependency. There are three ways to initiate this process for caches in a virtual network:
Migrate to a new cache using Private Links.
Create a new cache that uses Private Link for network isolation rather than virtual network injection and migrate your data to this cache. This option gives you the best and most secure network isolation experience, while also ensuring that all new caches are created using updated infrastructure.
Migrate to a new cache in a new Azure Resource Manager VNet subnet.
Creating a cache within a Classic VNet creates a Cloud Services (classic) cache and not an Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets cache. Migrating to a new cache in a new Azure Resource Manager VNet subnet fixes the underlying dependency on Cloud Services while maintaining a similar virtual network experience.
We have migrated most caches from being built on Cloud Services (classic) to being built on Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets. To migrate, delete the existing cache and create a new cache in a new Azure Resource Manager VNet subnet. We highly recommend not using old subnets while migrating caches. For recommended options for migrating the data in the cache, see Migrate to Azure Cache for Redis.
Automatic migration with data loss (recommended).
We're able to migrate caches from using Cloud Services (classic) to using Virtual Machine Scale Sets automatically, with cache configuration (include access keys and hostname) preserved. However, this method requires around 30 minutes of downtime and complete loss of data on the cache. You can use the import/export feature to save a copy of your data before the migration.
To utilize this option, contact [email protected] or create a support request to request a migration.
My cache isn't using VNet injection, but I received notice that I need to migrate. What should I do?
Check to see if your cache is using geo-replication. If so, you must migrate your data from your current geo-replicated pair to a fresh geo-replicated pair.
For example:
- Create a new geo-replicated pair of Premium caches that match the same configuration as your current pair of caches.
- Unlink your original pair of geo-replicated caches and export an RDB file from the primary cache.
- Import the RDB file into the primary cache in your new geo-replicated pair.
The new pair of geo-replicated caches won't have the same dependency on Cloud Services.
What should I do if I'm unable to create a new cache instance with the error message "the subnet is affected by Cloud Services retirement"?
We're starting to block the creation of new caches using the Cloud Services (classic) deployment model. New caches can still be created using this old deployment model if they're created in a virtual network subnet that once contained a Cloud Services cache, or if a cache is deployed into a classic VNet. If you see this message, create a new subnet in your VNet in which to deploy your cache. Creating a subnet in your virtual network ensures that a cache is created without the Cloud Services dependency.
To check if you have one or more Cloud Services based caches in your subnet, you can check Azure Advisor in the portal or use the resource-navigation-links REST API.
Use the resource-navigation-links API with your subscription ID, resource group name, virtual network name, and subnet name to get any caches in that subnet that are using Cloud Services.
If you're creating a new cache using the REST API, also ensure that you aren't passing the redis-configuration {"CacheVmType": "CloudService"} along with the create request. That parameters is an undocumented parameter, so it's unlikely you're doing this.
If you need to create new caches using the Cloud Services (classic) deployment model, contact [email protected] or create a support request to request an exemption.
What happens if caches aren't upgraded/migrated by August 31, 2024?
These caches will be shut down, and you lose any data in your caches.
What is the timeline for support?
Retirement occurs in three phases so that you have the maximum amount of time to migrate:
Active Stage (now to April 30, 2023)
Caches have full support, with no change in status from today. This period is given to allow customers time to transition off Cloud Service (classic) with minimal interruption.
Maintenance Stage (May 1, 2023 to December 31, 2023)
Caches will receive critical security, stability, and bug fixes, but no new features.
Inactive Stage (January 1, 2024 to August 31, 2024)
Caches receive only critical security fixes. All customers with support issues are required to migrate to a VMSS-based cache before receiving support. Customers must move off their caches by August 31, 2024.

Does this timeline apply to caches running on Redis 4.0?
No. This timeline only applies to caches running on Redis 6.0. Redis 4.0 is a part of a separate retirement that finishes before the Cloud Services (classic) retirement. All remaining caches using Redis 4.0 on Cloud Services (classic) will be automatically migrated to use Virtual Machine Scale Sets and Redis 6.0 after 31 October 2023. This migration method requires downtime and full data loss on the cache, so migrate ahead of this date if you'd like to avoid the downtime or data loss. Contact [email protected] or create a support request to request an automatic upgrade before 31 October 2023.
Where can I get more information if I have more questions about this retirement?
Post any of your questions to the Q&A page for Cloud Services (classic) retirement. Also, You can send email to [email protected] for more information.
General questions
What if my Azure Cache for Redis question isn't answered here?
If your question isn't listed here, let us know so we can help you find an answer.
To reach a wider audience, you can post a question on the Microsoft Q&A question page for Azure Cache and engage with the Azure Cache team and other members of the community.
If you want to make a feature request, you can submit your requests and ideas to Azure Cache for Redis User Voice.
You can also send your question to us at [email protected].