Примечание
Для доступа к этой странице требуется авторизация. Вы можете попробовать войти или изменить каталоги.
Для доступа к этой странице требуется авторизация. Вы можете попробовать изменить каталоги.
При создании агента вы также создаете приложение для Microsoft 365. Приложения для Microsoft 365 используют общую схему манифеста и формат упаковки, а также унифицированные процессы и средства распространения и управления. В конечном итоге приложения и агенты достигают максимально широкой аудитории и отображаются контекстно в рабочем процессе пользователей.
В этой статье описываются ключевые части модели приложений Microsoft 365, которые применяются к разработке агента.
Важно!
- Подключаемые модули API в настоящее время поддерживаются только в качестве действий в декларативных агентах. Они не включены в Microsoft 365 Copilot. Пример добавления подключаемого модуля API к декларативному агенту см. в разделе Добавление подключаемого модуля API в качестве настраиваемого действия для агента.
- Эта возможность включена по умолчанию во всех клиентах с лицензией Microsoft 365 Copilot. Администраторы могут отключить эту функцию на уровне пользователей и групп, а также контролировать, как отдельные подключаемые модули утверждаются для использования и какие подключаемые модули включены. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Управление агентами в интегрированных приложениях.
Пакет приложения
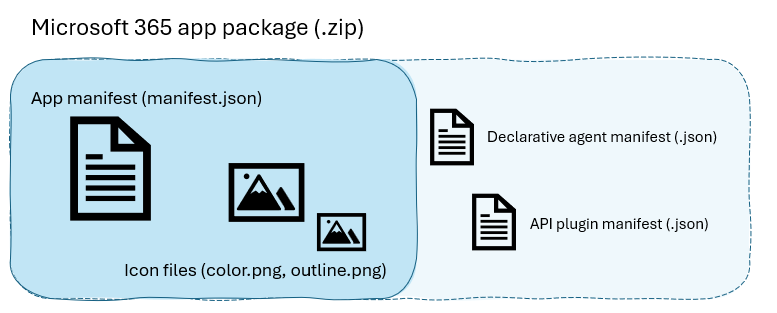
Пакет приложения для Microsoft 365, включая агенты, представляет собой ZIP-файл, содержащий один или несколько файлов конфигурации (манифеста) и значки вашего приложения. Логика приложения и хранилище данных размещаются в другом месте и получают доступ к ведущему приложению Microsoft 365 по протоколу HTTPS. Вы отправите пакет приложения администратору для публикации в организации или в Центр партнеров для публикации в Microsoft AppSource.
Как минимум, пакет приложения содержит:
-
Манифест приложения (
manifest.json), описывающий конфигурацию приложения, возможности, необходимые ресурсы и важные атрибуты. -
Большой значок цвета (
color.png), полноцветный значок 92x92 для отображения агента в пользовательском интерфейсе Microsoft 365 Copilot и хранения -
Небольшой значок контура (
outline.png), значок 32x32 с прозрачным фоном (в настоящее время не используется в Copilot, но требуется для прохождения проверки)
Пакет приложения также может содержать декларативные определения агента и подключаемого модуля API, а также файлы локализации для других поддерживаемых языков.
Значки приложений
Пакет приложения должен содержать цветную и структурную версию значка приложения, так как .png файлы. Эти значки имеют определенные требования к размеру для прохождения проверки в магазине.
Примечание.
В настоящее время только значок цвета используется для представления агентов пользователям (как в виде описания в магазине, так и в пользовательском интерфейсе Microsoft 365 Copilot), но при отправке пакета приложения в Microsoft AppSource по-прежнему требуется значок структуры.
Рекомендации по проектированию цветных и контурных значков для пакета приложений Microsoft 365 см . в разделе Значки приложений для Магазина Teams и панели приложения.
Цветной значок
Значок цвета представляет вашего агента в пользовательском интерфейсе Microsoft 365 Copilot и в магазинах приложений (Teams, Outlook, Microsoft 365).
![]()
Значок цвета:
- Может быть любым цветом
- Размер должен быть 192 x 192 пикселей
- Должен содержать символ 96 x 96 пикселей (чтобы разрешить заполнение 48 пикселей для сценариев размещения, где он обрезается)
- Должен располагаться на вершине полностью сплошного или полностью прозрачного квадратного фона
Контурный значок
Значок структуры используется для представления закрепленных и (или) активных приложений на панели приложений Teams. В настоящее время он не используется для агентов, но по-прежнему требуется для того, чтобы пакет приложения прошел проверку.
![]()
Значок структуры:
- Должно быть 32 x 32 пикселей
- Должен быть либо белым с прозрачным фоном, либо прозрачным с белым фоном
- Не должен содержать дополнительных заполнений вокруг символа
Манифест приложения
Манифест приложения для Microsoft 365 представляет собой JSON-файл, в котором описываются функции и характеристики приложения. По своей сути манифест приложения для Microsoft 365 — это схема для создания приложений Teams; однако, начиная с версии 1.13, она поддерживает приложения, которые работают на узлах Microsoft 365, в дополнение к Teams.
Если вы используете Copilot Studio для создания декларативного агента, манифест приложения создается на основе информации, предоставленной во время создания.
Каждый манифест приложения должен содержать следующие поля.
| Поле манифеста | Описание |
|---|---|
| version | Номер версии приложения в формате MAJOR. НЕСОВЕРШЕННОЛЕТНИЙ. PATCH (стандарт semver ). |
| id | Уникальный идентификатор, созданный для этого приложения на портале регистрации приложений Майкрософт (apps.dev.microsoft.com) в форме GUID. |
| разработчик | Сведения о разработчике, включая имя, веб-сайт и ссылки на политику конфиденциальности и условия использования. Для приложений, отправленных в AppSource, значения должны соответствовать значению, указанному в форме отправки приложений Центра партнеров. |
| name | Имя приложения, отображаемое для конечных пользователей в узле приложения. |
| description | Краткие и длинные описания приложения для пользователей. Для приложений, отправляемых в AppSource, эти значения должны совпадать с данными в записи AppSource. |
| Иконки | Относительные пути к файлам значков цвета и структуры. |
| accentColor | Цвет, используемый с и в качестве фона для значков структуры, в шестнадцатеричном значении RGB, например #4464ee. |
| Определения для конкретных возможностей приложений | Определение для каждой возможности приложения, например личных вкладок (staticTabs), расширений сообщений (composeExtensions) или ботов. Декларативные агенты и подключаемые модули API определяются в узле copilotAgents . |
В следующем примере показан манифест приложения с заполнителями в конце для расширения сообщений и возможностей приложения декларативного агента.
{
"$schema": "https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/json-schemas/teams/v1.18/MicrosoftTeams.schema.json",
"manifestVersion": "1.18",
"version": "1.0.0",
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000",
"developer": {
"name": "Northwind Traders",
"websiteUrl": "https://www.example.com",
"privacyUrl": "https://www.example.com/termofuse",
"termsOfUseUrl": "https://www.example.com/privacy"
},
"icons": {
"color": "Northwind-Logo-196.png",
"outline": "Northwind-Logo-32.png"
},
"name": {
"short": "Northwind Inventory",
"full": "Northwind Inventory App"
},
"description": {
"short": "App allows you to find and update product inventory information",
"full": "Northwind Inventory is the ultimate tool for managing your product inventory. With its intuitive interface and powerful features, you'll be able to easily find your products by name, category, inventory status, and supplier city. You can also update inventory information with the app."
},
"accentColor": "#3690E9",
"composeExtensions": {
...
},
"copilotAgents": {
...
}
}
Дополнительные сведения см. в справочнике по манифесту приложения Microsoft 365.
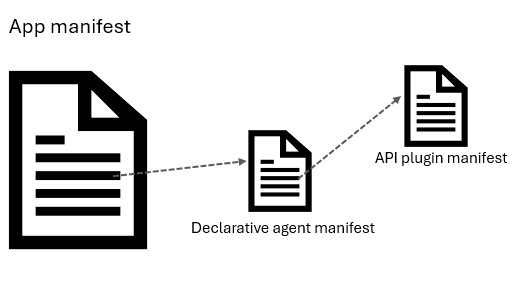
copilotAgents Определения
Декларативные агенты и подключаемые модули API имеют собственные схемы определений. Файл определения декларативного агента ссылается из объекта copilotAgents манифеста приложения.
В следующем примере показано, как ссылаться на декларативный агент:
"copilotAgents": {
"declarativeAgents": [
{
"id": "agent1",
"file": "declarativeAgent1.json"
}
]
},
На определение подключаемого модуля API ссылается (в разделе actions) из определения декларативного агента.
Обратите внимание на следующее:
В настоящее время поддерживается только одно декларативное определение агента для каждого манифеста приложения.
При использовании Copilot Studio для создания агентов для каждого из них создается уникальный
idобъект в рамках общего создания манифеста приложения. При создании агентов с помощью Microsoft 365 Agents Toolkit (эволюция набора средств Teams) или собственной интегрированной среды разработки вы назначаетеidсебе в соответствии с собственными соглашениями или понятным именем.
Манифест декларативного агента
Манифест декларативного агента содержит инструкции для ответов Copilot, примеры запросов для начала беседы, источники данных, используемые для заземления, а также список действий (навыки подключаемого модуля API), которые агент может выполнить.
Дополнительные сведения см. в статье Схема манифеста декларативного агента для Microsoft 365 Copilot.
Манифест подключаемого модуля API
Манифест подключаемого модуля API описывает возможности подключаемого модуля, включая поддерживаемые им API и операции, которые он может выполнять. Он также содержит метаданные, такие как имя, описание, версия, а также ссылку на определение OpenAPI интерфейсов REST API, с которыми он взаимодействует. На подключаемые модули API можно ссылаться из манифеста декларативного агента, который будет использоваться в интерфейсе декларативного агента.
Дополнительные сведения см. в статье Схема манифеста подключаемого модуля API для Microsoft 365 Copilot.