Примечание.
Для доступа к этой странице требуется авторизация. Вы можете попробовать войти или изменить каталоги.
Для доступа к этой странице требуется авторизация. Вы можете попробовать изменить каталоги.
В этой статье приведены пошаговые инструкции по созданию реплики чтения гибкого экземпляра сервера Базы данных Azure для PostgreSQL.
Замечание
При развертывании реплик чтения для постоянных нагрузок с интенсивной записью основная задержка репликации может продолжать увеличиваться и никогда не догонит основной сервер. Он также может увеличить использование хранилища на основном сервере, так как WAL-файлы удаляются только после получения на реплике.
Это важно
Ознакомьтесь с разделом 'Рекомендации' в обзорной статье о репликах для чтения.
Прежде чем изменять значения следующих параметров сервера на основном сервере, сначала измените их на репликах для чтения. При этом вы избегаете проблем во время повышения реплики для чтения на первичную: max_connections, max_prepared_transactions, max_locks_per_transaction, max_wal_senders, max_worker_processes.
Перед настройкой реплики чтения для гибкого экземпляра сервера Базы данных Azure для PostgreSQL убедитесь, что основной сервер настроен на соответствие необходимым предварительным требованиям. Определенные параметры на основном сервере могут повлиять на возможность создания реплик.
Автоматическое увеличение хранилища. Параметры автоматического увеличения хранилища на основном сервере и его репликах чтения должны соответствовать определенным рекомендациям, чтобы обеспечить согласованность и предотвратить нарушения репликации. Чтобы получить подробные правила и параметры, ознакомьтесь с автоматическим расширением хранилища .
Тип хранилища: реплики чтения можно создавать только на серверах, настроенных для использования типа хранилища SSD уровня "Премиум". Если для рабочей нагрузки требуются реплики чтения, убедитесь, что основной сервер создается с данным типом хранилища.
Шаги по созданию реплики для чтения
Использование портала Azure:
Выберите гибкий экземпляр сервера Базы данных Azure для PostgreSQL, который вы хотите использовать в качестве основного сервера.
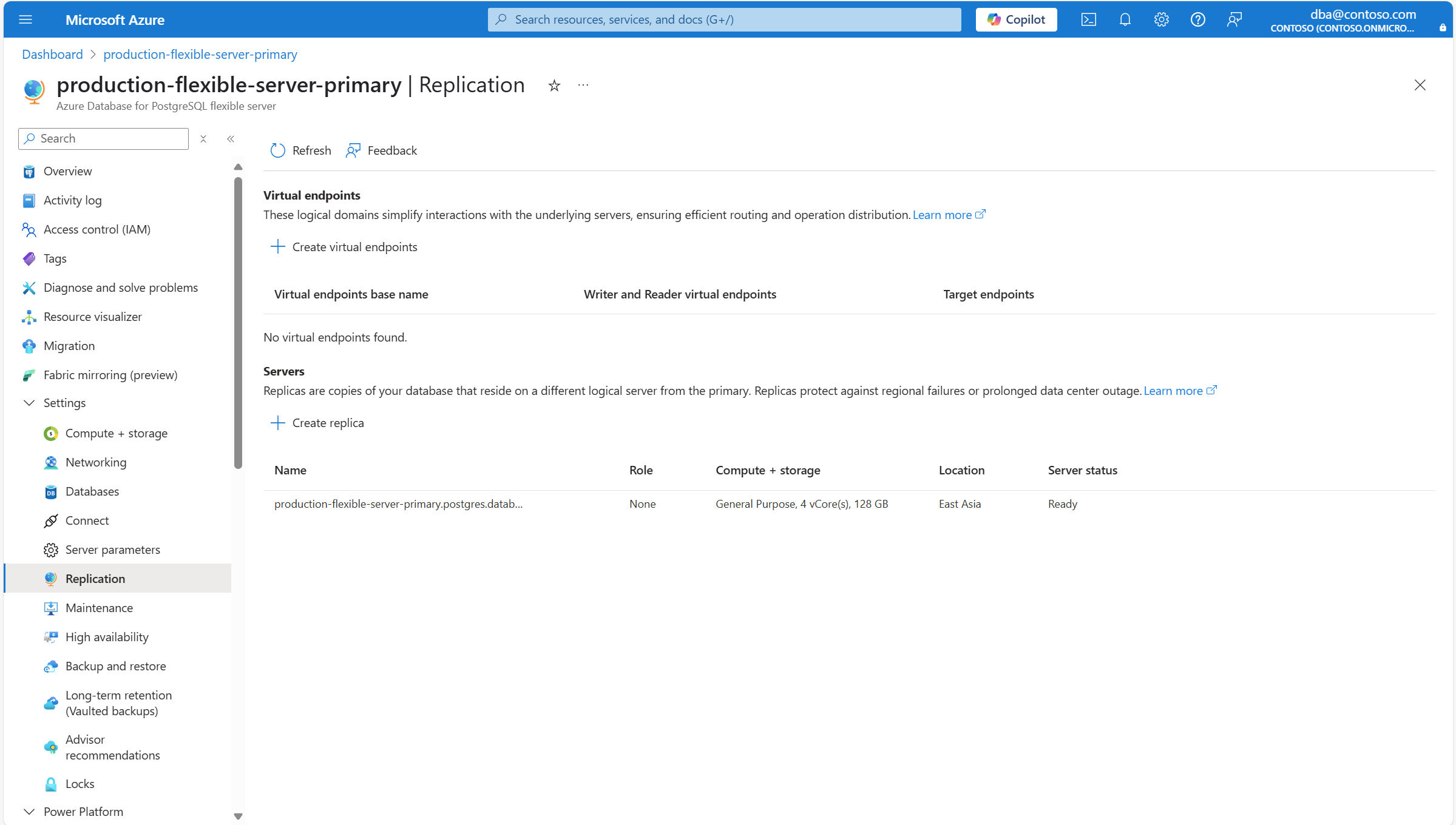
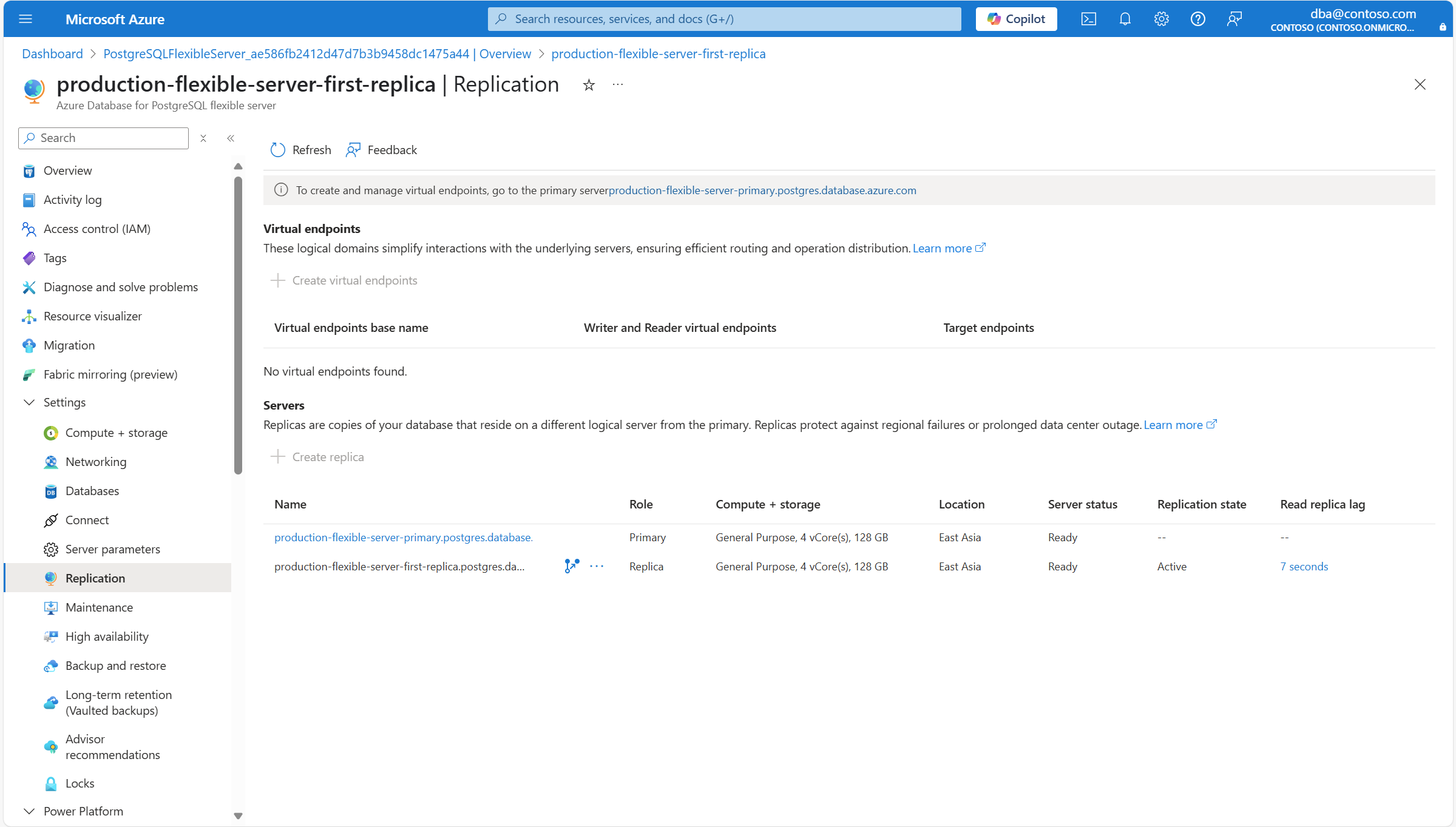
В меню ресурсов в разделе "Параметры " выберите "Репликация".
В разделе "Серверы" выберите "Создать реплику".
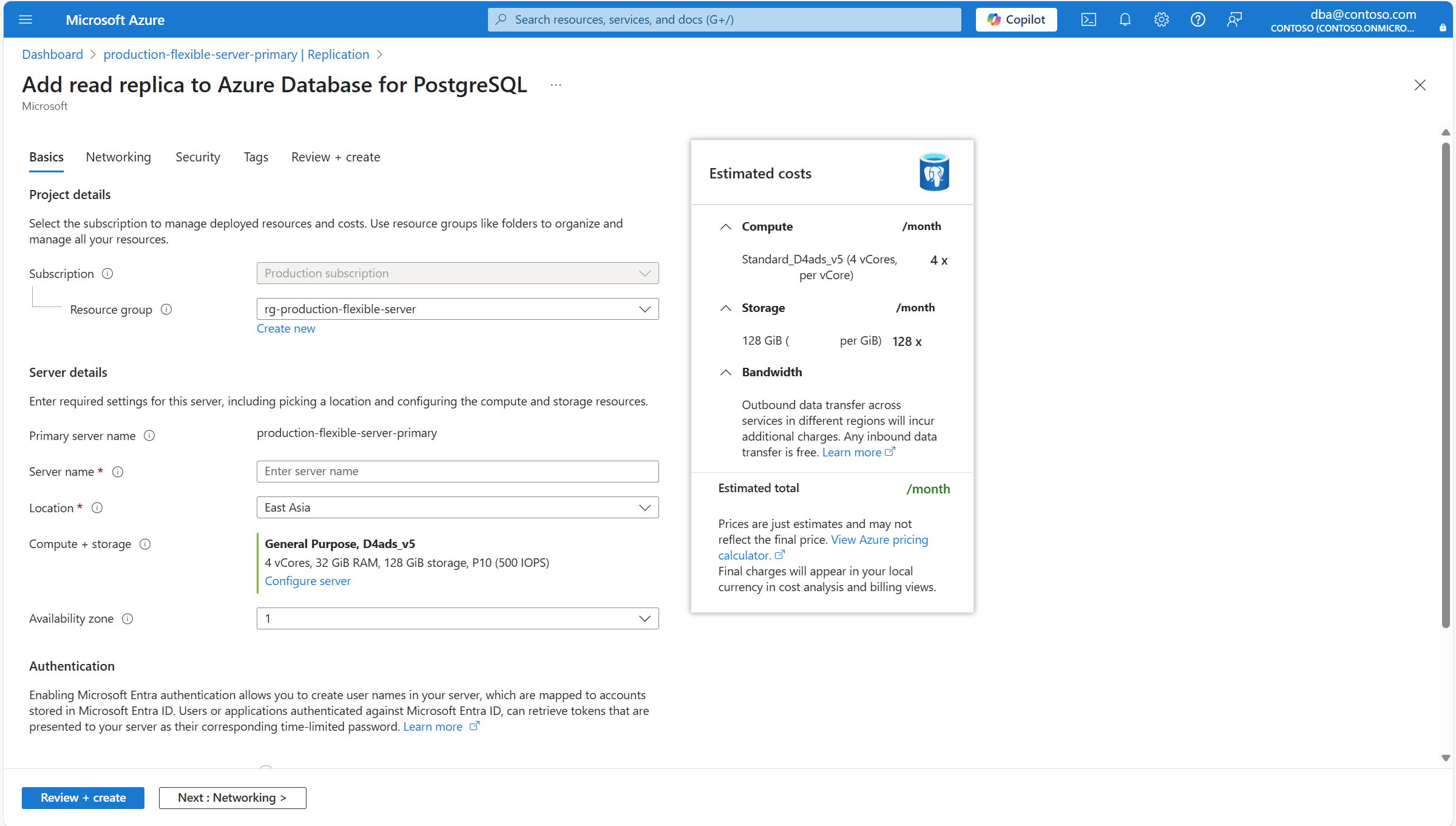
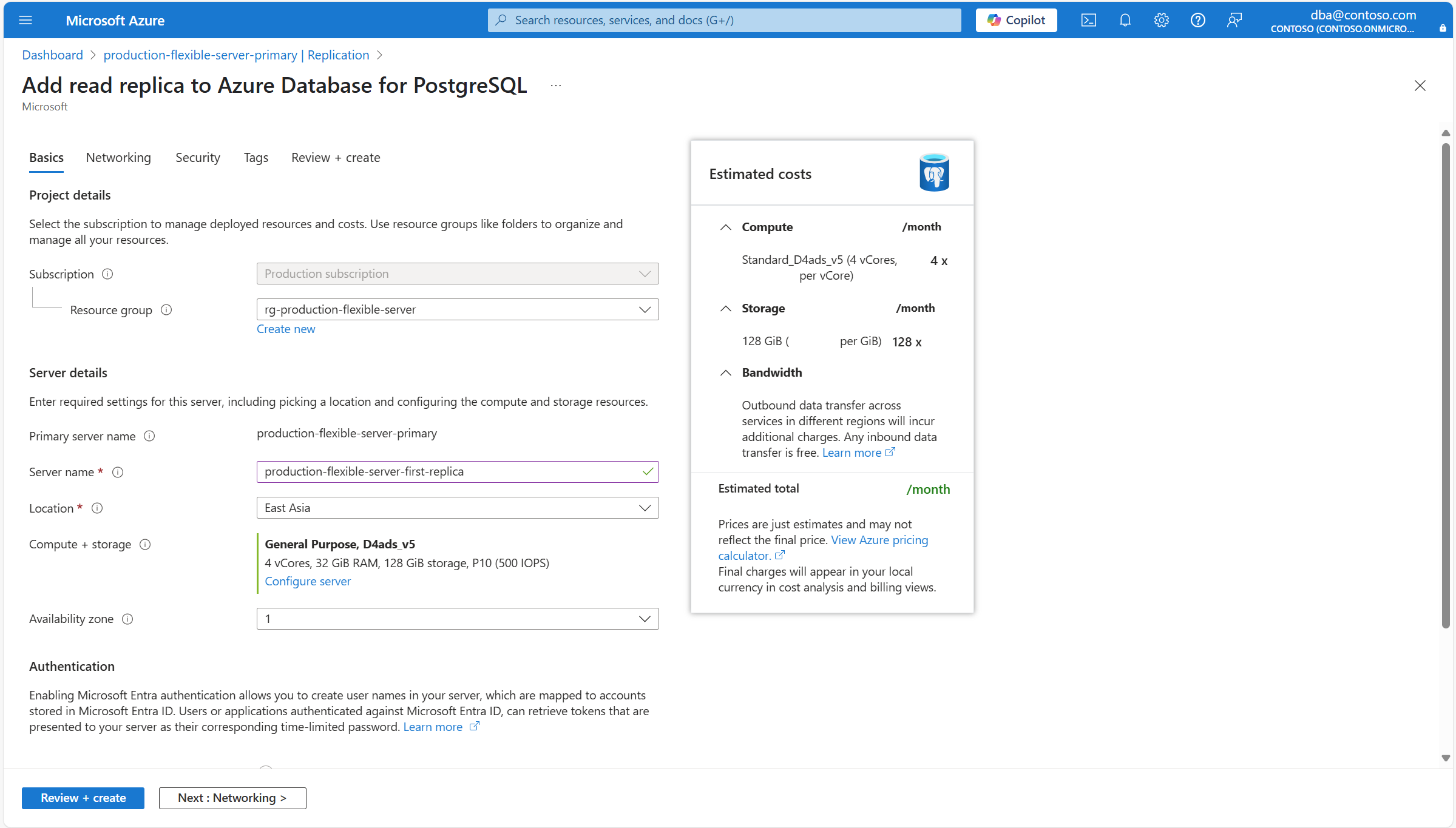
Вы перенаправляетесь в мастер добавления реплики чтения в базу данных Azure для PostgreSQL , из которой можно настроить некоторые параметры для созданной реплики чтения.
Используйте следующую таблицу, чтобы понять смысл различных полей, доступных на странице "Основы ", и в качестве руководства для заполнения страницы.
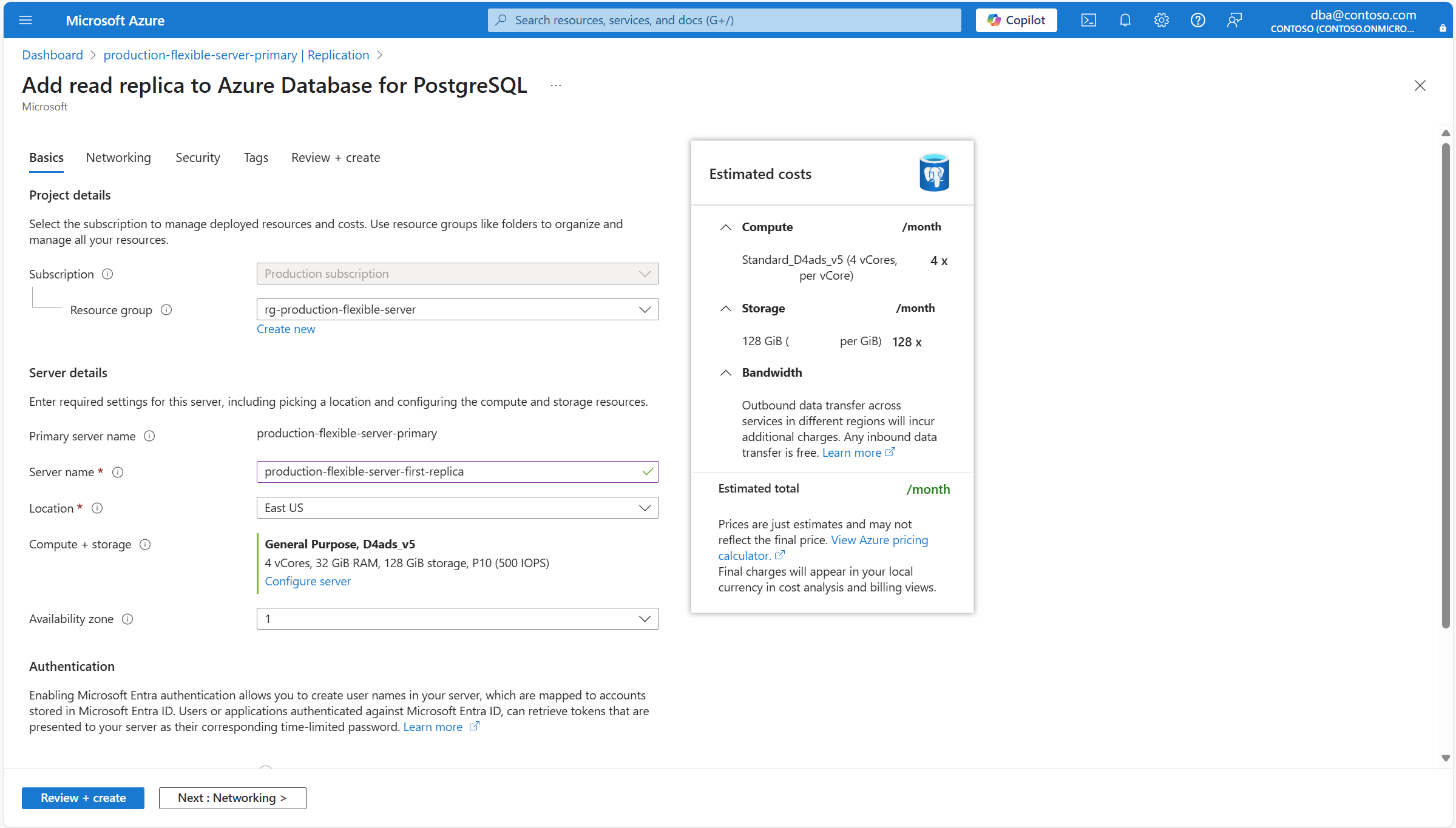
Секция Setting Рекомендуемое значение Description Возможны изменения после создания экземпляра Сведения о проекте Subscription Имя подписки, в которой вы хотите создать ресурс. Подписка — это соглашение с Корпорацией Майкрософт об использовании одной или нескольких облачных платформ или служб Майкрософт, для которых взимается плата за лицензию на пользователя или использование облачных ресурсов. Существующий гибкий сервер базы данных Azure для PostgreSQL можно переместить в другую подписку, отличную от той, в которой он был первоначально создан. Дополнительные сведения см. в статье "Перемещение ресурсов Azure в новую группу ресурсов или подписку". Группа ресурсов Группа ресурсов в выбранной подписке, в которой требуется создать ресурс. Это может быть существующая группа ресурсов, или вы можете выбрать Создать новую и указать имя в этой подписке, уникальное среди существующих имен групп ресурсов. Группа ресурсов — это контейнер, содержащий связанные ресурсы для решения Azure. В группу ресурсов могут входить все ресурсы приложения или только те, которыми необходимо управлять совместно. Вы решите, как вы хотите выделить ресурсы группам ресурсов на основе того, что имеет наибольшее значение для вашей организации. Как правило, добавьте ресурсы, которые совместно используют один и тот же жизненный цикл в одну и ту же группу ресурсов, чтобы легко развернуть, обновить и удалить их как группу Существующий гибкий сервер базы данных Azure для PostgreSQL можно переместить в другую подписку, отличную от той, в которой он был первоначально создан. Дополнительные сведения см. в статье "Перемещение ресурсов Azure в новую группу ресурсов или подписку". Сведения о сервере Имя сервера-источника Имя основного сервера, для которого вы пытаетесь создать реплику для чтения. Уникальное имя, идентифицирующее гибкий серверный экземпляр Azure Database for PostgreSQL. Доменное имя postgres.database.azure.comдобавляется к указанному вами имени сервера, чтобы составить полное имя узла, с помощью которого можно использовать сервер системы доменных имен для разрешения IP-адреса вашего экземпляра.Имя сервера Имя, которое необходимо назначить новой реплике чтения. Уникальное имя, идентифицирующее гибкий серверный экземпляр Azure Database for PostgreSQL. Доменное имя postgres.database.azure.comдобавляется к указанному вами имени сервера, чтобы составить полное имя узла, с помощью которого можно использовать сервер системы доменных имен для разрешения IP-адреса вашего экземпляра.Хотя имя сервера не может быть изменено после создания сервера, можно использовать функцию восстановления точки во времени, чтобы восстановить сервер под другим именем. Альтернативный подход к продолжению использования существующего сервера, но при этом можно ссылаться на него по другому имени сервера, использует виртуальные конечные точки, чтобы создать точку доступа записи с новым нужным именем. Этот подход позволяет ссылаться на экземпляр по его исходному имени или по имени, назначенному виртуальной конечной точке записи. Местоположение Имя одного из регионов, в которых поддерживается служба. Восстановление на момент времени поддерживает только развертывание нового сервера в том же регионе, в котором существует исходный сервер. Соответствие требованиям, расположение данных, цены, близость к пользователям или доступность других служб в том же регионе являются некоторыми из требований, которые следует использовать при выборе региона. Сервис не предлагает возможность автоматически и прозрачно перемещать экземпляр в другой регион. Вычисления и хранение Назначает тот же тип и размер вычислительных ресурсов и тот же размер хранилища, что и исходный сервер во время восстановления резервной копии. Однако, если вы выберете ссылку "Настройка сервера", вы можете изменить тип хранилища, выделенного для нового сервера, и выбрать, нужно ли его оснастить геоизбыточными резервными копиями. После развертывания нового сервера его параметры вычислений можно масштабировать вверх или вниз. Зона доступности Предпочитаемая зона доступности. Вы можете выбрать зону доступности, в которой будет развернут сервер. Возможность выбрать зону доступности, в которой будет развернут ваш экземпляр, полезна для размещения его вместе с вашим приложением. Если вы выберете "Нет предпочтения", вашему экземпляру автоматически присваивается зона доступности по умолчанию во время его создания. Хотя зона доступности, в которой развертывается экземпляр, не может быть изменена после его создания, можно использовать функцию восстановления точки во времени для восстановления сервера под другим именем в другой зоне доступности. Аутентификация Эти параметры являются только информационными. Все настройки, связанные с проверкой подлинности, используемой для реплики чтения, наследуются от основного сервера. Можно изменить на основном сервере, и изменения коснутся как его, так и всех существующих реплик чтения. Если вы хотите изменить уровень вычислений, процессор или размер, автоматически назначенный новому серверу, или если вы хотите изменить некоторые параметры хранилища реплики чтения, выберите "Настроить сервер".
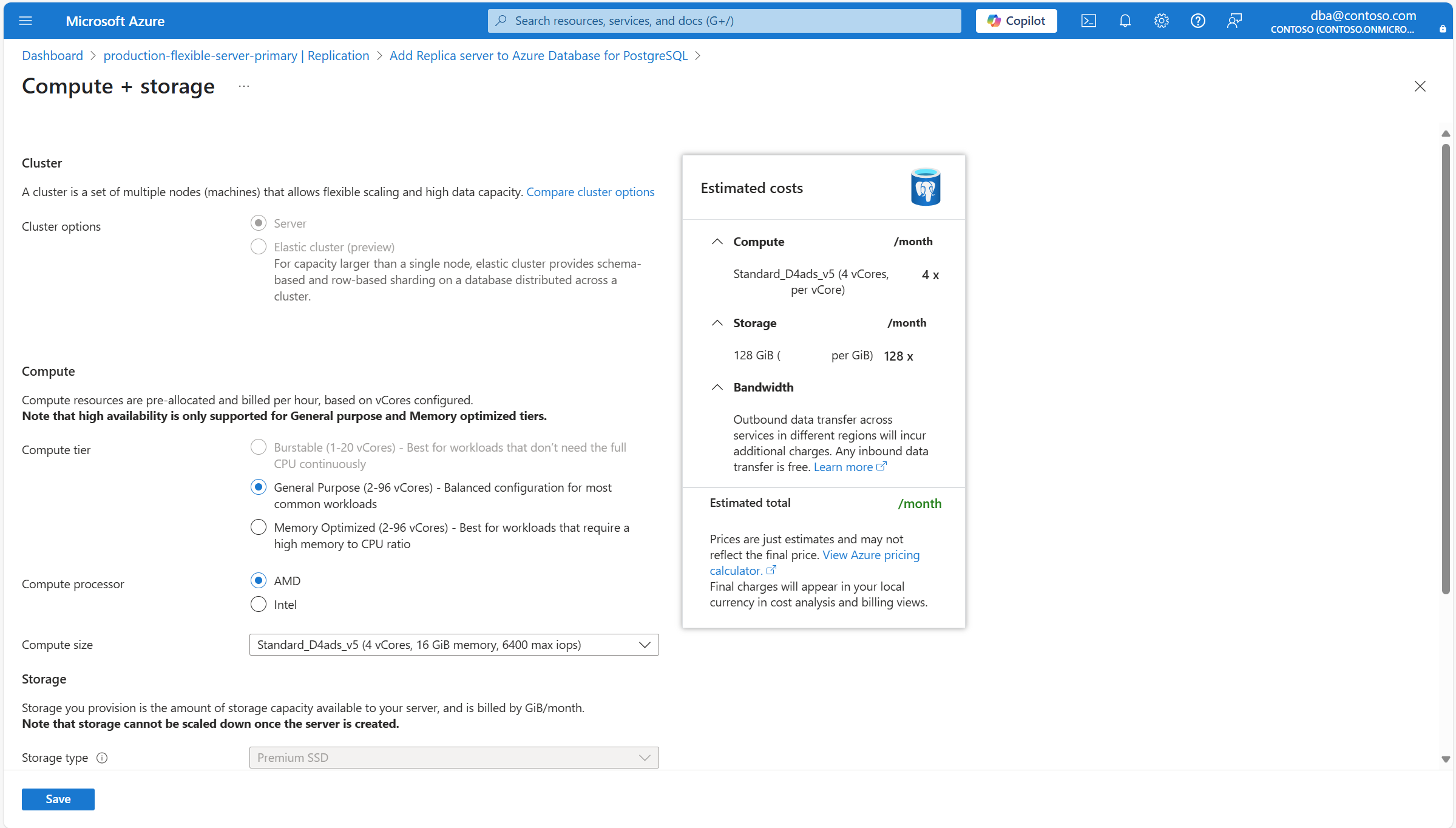
Откроется Вычисление + хранилище и отображает параметры вычислений и хранения для нового сервера.
Используйте следующую таблицу, чтобы понять смысл различных полей, доступных на странице вычислений и хранилища , и в качестве руководства по заполнению страницы.
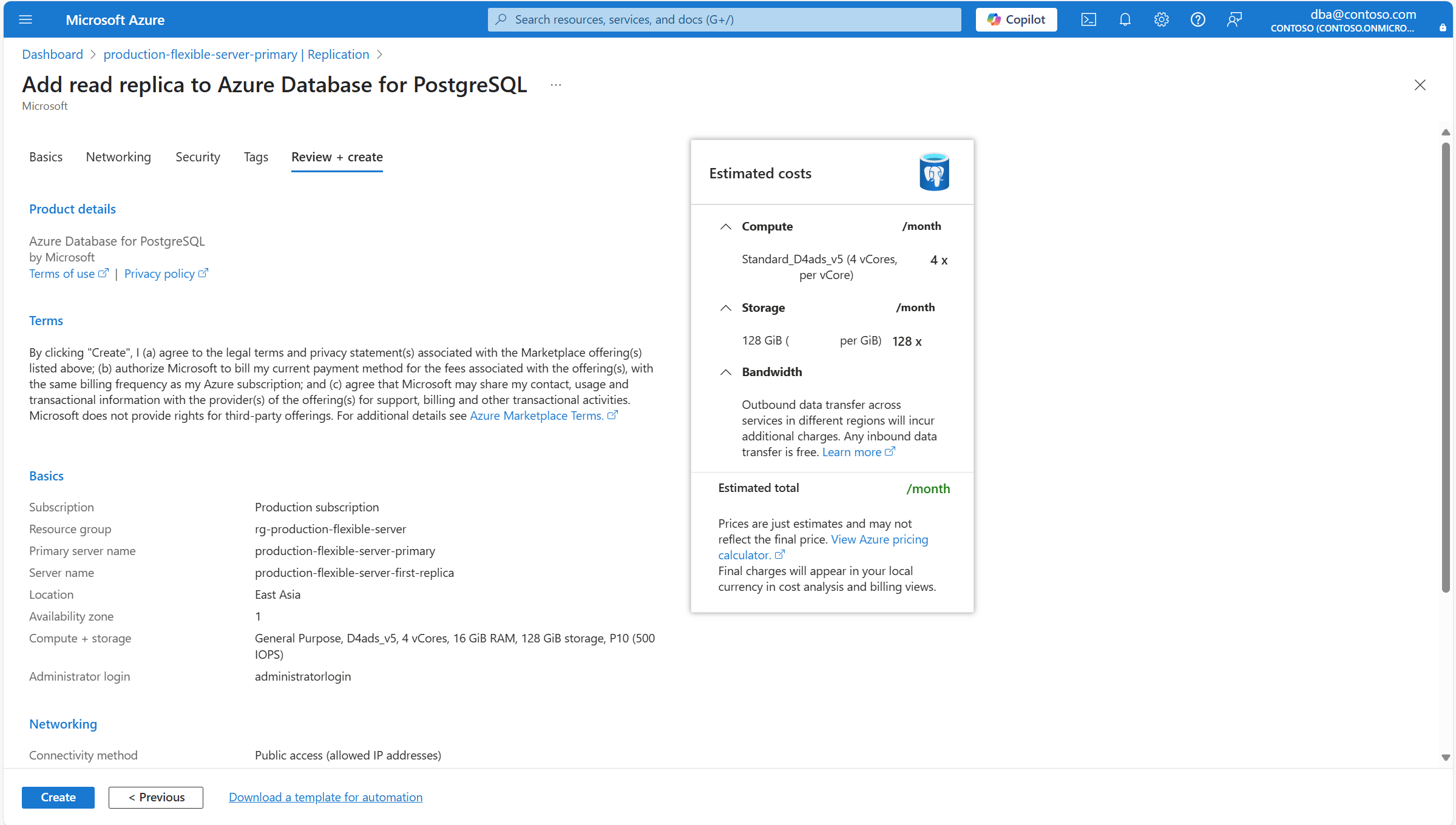
Секция Setting Рекомендуемое значение Description Можно изменить после создания читаемой реплики Вычисление Уровень вычислений По умолчанию он автоматически устанавливается на тот же уровень, назначенный основному серверу. Однако его можно задать для любого другого уровня вычислительных ресурсов, на котором поддерживаются реплики чтения. Возможные значения: "Общее назначение " (обычно используется для рабочих сред с наиболее распространенными рабочими нагрузками) и оптимизировано для памяти (обычно используется для рабочих сред, работающих в рабочих средах, требующих высокой памяти к коэффициенту ЦП). Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе "Параметры вычислений" в Базе данных Azure для PostgreSQL. Можно изменить после создания читаемой реплики. Однако если вы используете некоторые функции, которые поддерживаются только на определенных уровнях, и измените текущий уровень на один, в котором функция не поддерживается, функция перестает быть доступна или отключена. Размер вычислительных ресурсов По умолчанию он автоматически устанавливается на тот же размер вычислительных ресурсов, назначенный основному серверу. Однако вы можете задать для него любой другой размер вычислительных ресурсов, если он имеет то же или более высокое количество виртуальных ядер, что и основной сервер. Обратите внимание, что список поддерживаемых значений может отличаться в разных регионах в зависимости от оборудования, доступного для каждого региона. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе "Параметры вычислений" в Базе данных Azure для PostgreSQL. Можно изменить после создания реплики для чтения. Хранение Тип хранилища Оставьте его так, как настроен SSD уровня "Премиум". Установка типа хранилища в значение, отличное от значения основного сервера, не поддерживается. Мастер автоматически задает это свойство в соответствии с типом хранилища, назначенным основному серверу. Невозможно изменить после создания реплики для чтения. Размер хранилища По умолчанию для него задано то же значение, что и размер хранилища первичного сервера. Однако его можно задать для любого более высокого значения. Можно изменить после создания экземпляра реплики данных для чтения. Можно увеличить только его. Ручное или автоматическое сжатие хранилища не поддерживается. Уровень производительности По умолчанию он автоматически устанавливается на то же значение, что и основной сервер. Однако его можно изменить на другое значение. Производительность твердотельных накопителей класса Premium (SSD) устанавливается при создании диска в виде уровня производительности. При настройке подготовленного размера диска автоматически выбирается уровень производительности. Этот уровень производительности определяет количество операций ввода-вывода в секунду и пропускную способность управляемого диска. Для дисков SSD уровня "Премиум" этот уровень можно изменить при развертывании или после этого без изменения размера диска и без простоя. Изменение уровня доступа позволяет подготовиться к более высокому уровню спроса, не используя возможности резервной производительности диска. Может оказаться более экономичным изменить уровень производительности, а не полагаться на всплеск, в зависимости от продолжительности необходимости в дополнительной производительности. Это идеально подходит для событий, которые временно требуют постоянно более высокого уровня производительности. Такие события, как праздничные покупки, тестирование производительности или запуск учебной среды. Для обработки этих событий можно переключить диск на более высокий уровень производительности без простоя до тех пор, пока вам потребуется дополнительная производительность. Затем вы можете вернуться на исходный уровень без простоя, когда дополнительная производительность больше не требуется. Можно изменить после создания экземпляра. Автоматическое увеличение хранилища Невозможно изменить и автоматически задать то же значение, что и исходный сервер. Обратите внимание, что этот параметр может не поддерживаться для некоторых типов хранилища, и он может не учитываться для определенных размеров хранилища. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе "Настройка автоматического увеличения хранилища". Можно изменить после создания экземпляра, если тип хранилища поддерживает эту функцию. Перейдите на вкладки "Сеть", "Безопасность" или "Теги ", если необходимо изменить любой из параметров, которые могут отличаться от основного сервера. После настройки всей новой реплики в соответствии с вашими потребностями нажмите кнопку "Проверить и создать".
Проверьте правильное установка всех конфигураций для нового развертывания и нажмите кнопку "Создать".
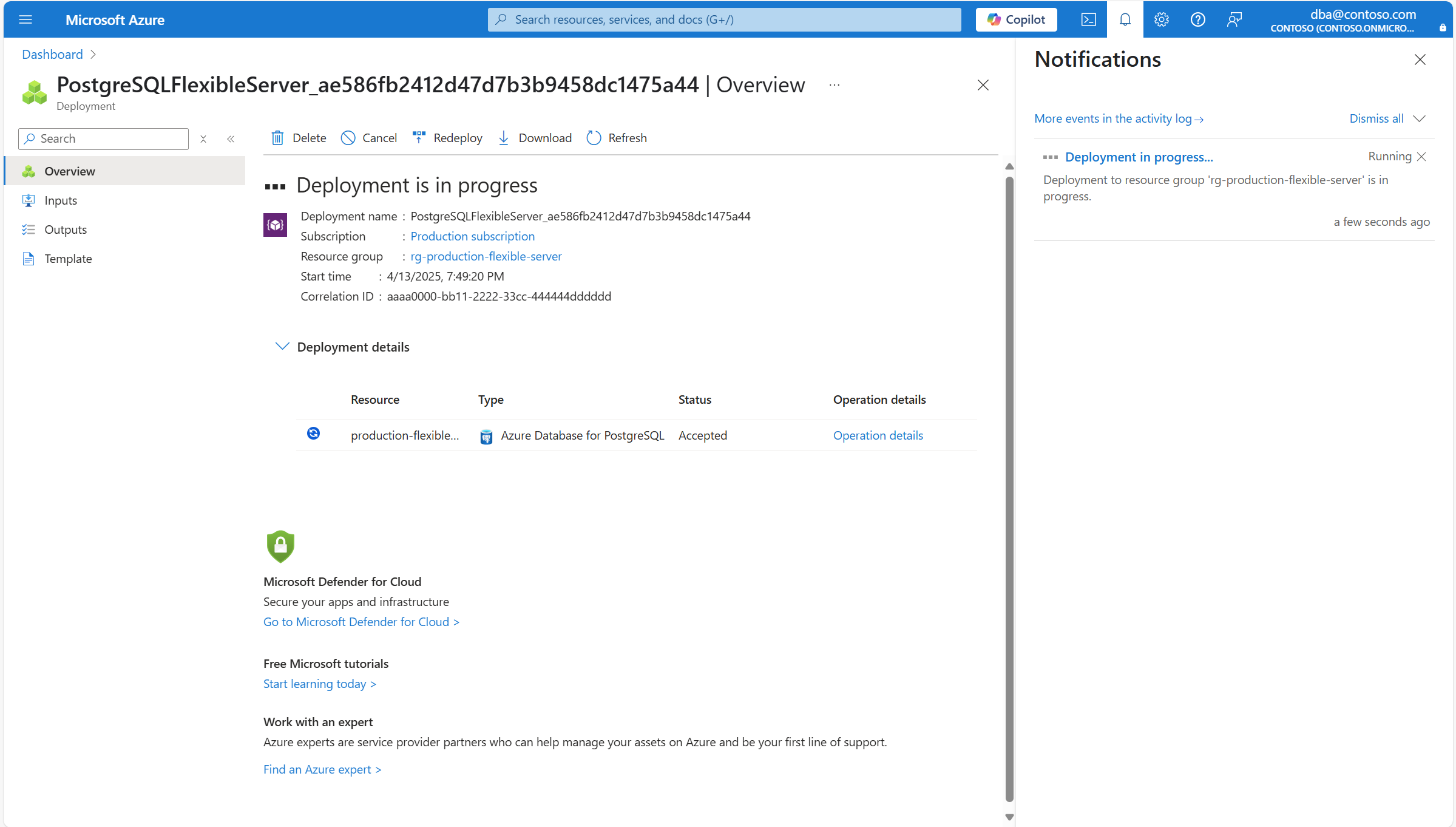
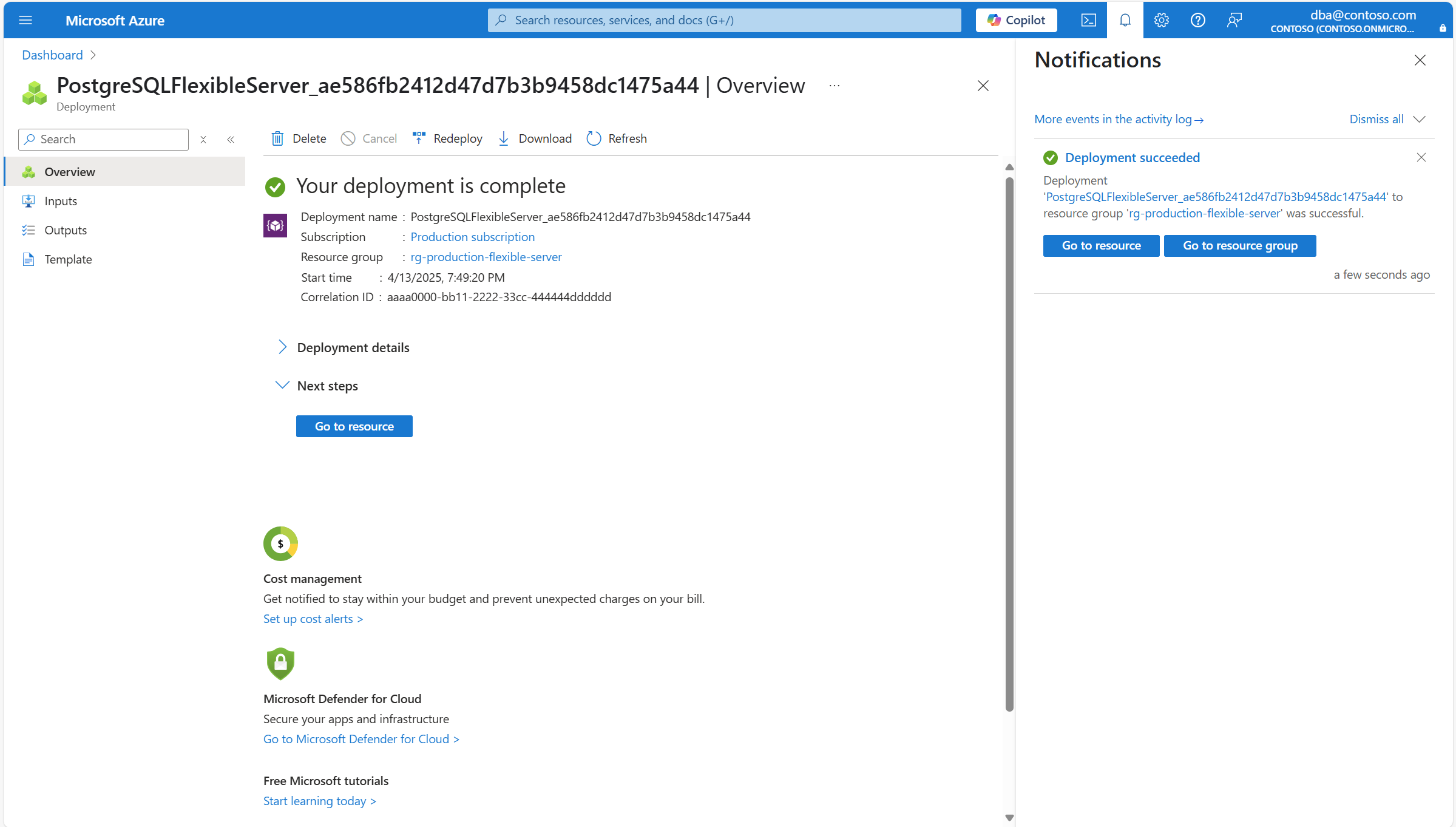
Запускается новое развертывание для создания нового гибкого экземпляра сервера базы данных Azure для PostgreSQL и превращения его в реплику для чтения основного сервера.
После завершения развертывания можно выбрать "Перейти к ресурсу", чтобы начать работу с новым экземпляром гибкого сервера базы данных Azure для PostgreSQL.
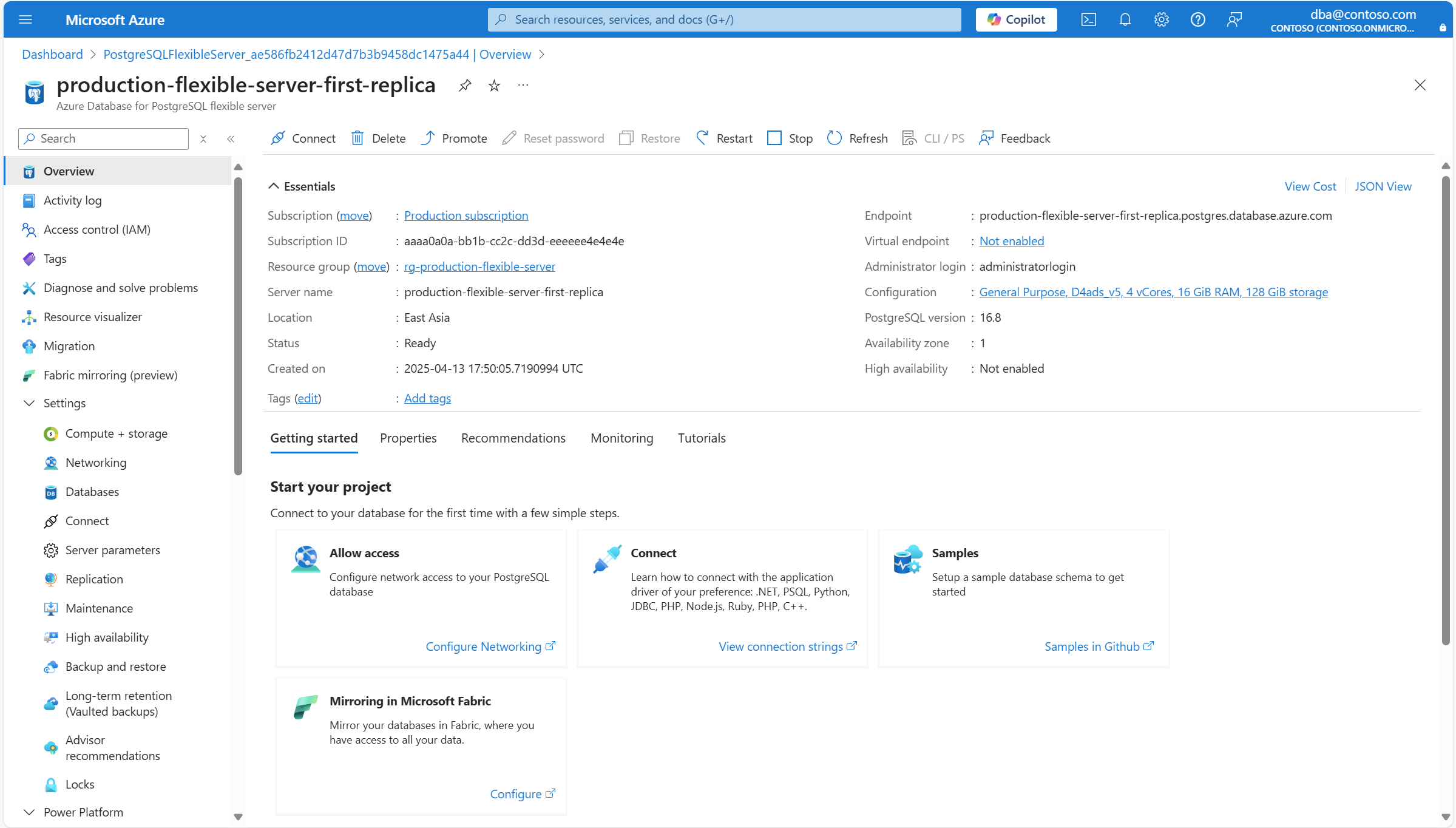
На страницу Обзор сервера-реплики.
В меню ресурсов в разделе "Параметры " выберите "Репликация". В разделе "Серверы" найдите список серверов, соответствующих набору репликации, и роль, которую принимает каждый из них.