Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In some cases, you might need to manually configure your C++ project to get IntelliSense working properly. For MSBuild projects (based on .vcxproj files), you can adjust settings in project properties. For non-MSBuild projects, you adjust settings in the CppProperties.json file in the root directory of the project. In some cases, you might need to create a hint file to help IntelliSense understand macro definitions. The Visual Studio IDE helps you identify and fix IntelliSense problems.
Single-file IntelliSense
When you open a file that isn't included in a project, Visual Studio provides some IntelliSense support, but by default no error squiggles are shown. If the Navigation Bar says Miscellaneous Files, then that probably explains why you don't see error squiggles under incorrect code, or why a preprocessor macro isn't defined.
Check the Error List
If a file isn't open in single-file mode, and IntelliSense isn't working correctly, the first place to check is the Error List window. To see all the IntelliSense errors for the current source file together with all included header files, choose Build + IntelliSense in the dropdown:

IntelliSense produces a maximum of 1,000 errors. If there are more than 1,000 errors in the header files included by a source file, then the source file shows only a single error squiggle at the very start of the source file.
Ensure #include paths are correct
MSBuild projects
If you run your builds outside of the Visual Studio IDE, and your builds are succeeding but IntelliSense is incorrect, it's possible that your command line is out of sync with the project settings for one or more configurations. Right-click on the project node in Solution Explorer and make sure that all #include paths are correct for the current configuration and platform. If the paths are identical in all configurations and platforms, you can select All configurations and All platforms and then verify that the paths are correct.
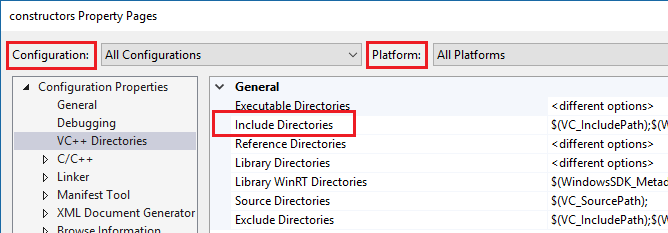
To see the current values for build macros such as VC_IncludePath, select the Include Directories dropdown. Then choose <Edit> and select the Macros button.
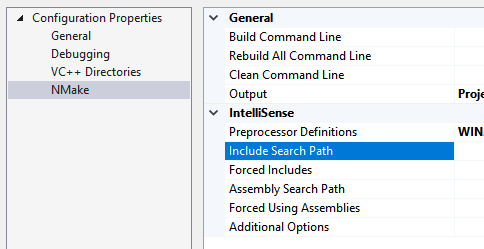
Makefile projects
For Makefile projects that are based on the NMake project template, choose NMake under Configuration Properties, and then choose Include search path in the IntelliSense category:
CMake projects
For CMake projects, make sure that #include paths are specified correctly for all configurations in CMakeLists.txt. Other project types might require a CppProperties.json file. For more information, see Configure code navigation with CppProperties.json. Make sure that the paths are correct for each configuration that is defined in the file.
If there's a syntax error in the CppProperties.json file, IntelliSense in the affected files is incorrect. Visual Studio displays the error in the Output Window.
Tag parser issues
The tag parser is a fuzzy C++ parser that's used for browsing and navigation. It's fast but doesn't attempt to completely comprehend every code construct.
For example, it doesn't evaluate preprocessor macros, and therefore it might incorrectly parse code that makes heavy use of them. When the Tag Parser encounters an unfamiliar code construct, it might skip that entire region of code.
There are two common ways in which this problem manifests in Visual Studio:
The IDE offers to create a function definition for a function that is already defined.
If the navigation bar shows an innermost macro, then the current function definition was skipped:
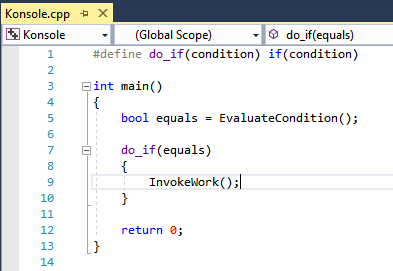
The code snippet shows a macro definition for do_if that is used inside of the function main. The tag parser doesn't understand the macro, so instead of the navigation dropdown showing that the name of the current function is main, it shows the name of the macro: do_if.
To fix these kinds of problems, add a file named cpp.hint to the root of your solution directory. For more information, see Hint Files.
Tag parser errors appear in the Error List window.
Validate project settings with diagnostic logging
To check whether the IntelliSense compiler is using correct compiler options, including Include Paths and Preprocessor macros, turn on Diagnostic Logging of IntelliSense command lines in Tools > Options > Text Editor > C/C++ > Advanced > Diagnostic Logging. Set Enable Logging to True, Logging Level to 5 (most verbose), and Logging Filter to 8 (IntelliSense logging).
The Output Window now shows the command lines that are passed to the IntelliSense compiler. Here's a sample output:
[IntelliSense] Configuration Name: Debug|Win32
[IntelliSense] Toolset IntelliSense Identifier:
[IntelliSense] command line options:
/c
/I.
/IC:\Repo\Includes
/DWIN32
/DDEBUG
/D_DEBUG
/Zc:wchar_t-
/Zc:forScope
/Yustdafx.h
This information might help you understand why IntelliSense is providing inaccurate information. For example, if your project's Include directory contains $(MyVariable)\Include, and the diagnostic log shows /I\Include as an Include path, it means that $(MyVariable) wasn't evaluated, and was removed from the final include path.
About the IntelliSense build
Visual Studio uses a dedicated C++ compiler to create and maintain the database that powers all the IntelliSense features. To keep the IntelliSense database in sync with the code, Visual Studio automatically launches IntelliSense-only builds as background tasks in response to certain changes made in the project settings or source files.
However, in some cases Visual Studio might not update the IntelliSense database in a timely manner. For example, when you run a git pull or git checkout command, Visual Studio might take up to an hour to detect changes in the files. You can force a rescan of all files in a solution by right-clicking on the project node in Solution Explorer and choosing Rescan Solution.
Troubleshoot IntelliSense build failures
An IntelliSense build doesn't produce binaries, but it can still fail. One possible cause for failure is custom .props or .targets files. In Visual Studio 2017 version 15.6 and later, IntelliSense-only build errors are logged to the Output window. To see them, set Show output from to Solution:

The error message might instruct you to enable design-time tracing:
error: Designtime build failed for project 'E:\src\MyProject\MyProject.vcxproj',
configuration 'Debug|x64'. IntelliSense might be unavailable.
Set environment variable TRACEDESIGNTIME=true and restart
Visual Studio to investigate.
If you set the environment variable TRACEDESIGNTIME to true and restart Visual Studio, you see a log file in the %TEMP% directory, which might help diagnose the build failure.
To learn more about TRACEDESIGNTIME environment variable, see Roslyn and Design-time builds. The information in these articles is relevant for C++ projects.