Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Note
After two months of inactivity, scheduled refresh on your semantic model is paused. For more information, see Scheduled refresh later in this article.
This article describes the options available for scheduled refresh for the On-premises data gateway (personal mode) and the On-premises data gateway. You specify refresh options in the following areas of the Power BI service: Gateway connection, Data source credentials, and Schedule refresh. We'll look at each in turn. For more information about data refresh, including limitations on refresh schedules, see Data refresh.
To get to the Schedule refresh screen:
Go to the workspace and select a semantic model from the workspace content list.
On the semantic model details page, select Refresh > Schedule refresh.

Gateway and cloud connections
You'll see different options here depending on whether you have a personal gateway or enterprise gateway online and available.
If no gateway is available, you'll see Gateway connection disabled. You'll also see a message indicating how to install the personal gateway.
If you have a personal gateway configured and it's online, it's available to select. It shows offline if it's not available.
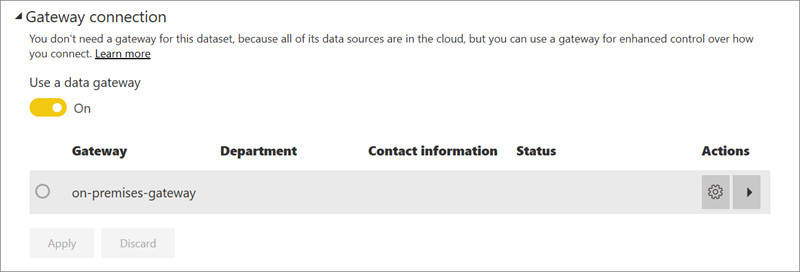
You can also select the enterprise gateway if one is available for you. You only see an enterprise gateway available if your account is listed in the Users tab of the data source configured for a given gateway.
Data source credentials
Power BI Gateway - Personal
If you're using the personal gateway to refresh data, you must supply the credentials to connect to the back-end data source. If you connected to an app from an online service, the credentials you entered to connect are carried over for scheduled refresh.

You're only required to sign in to a data source the first time you use refresh on that semantic model. Once entered, those credentials are retained with the semantic model.
Note
For some authentication methods, if the password you use to sign in to a data source expires or is changed, you need to change it for the data source in Data source credentials too.
If there's a problem, typically it's either the gateway is offline because it couldn't sign in to Windows and start the service, or Power BI couldn't sign in to the data sources to query for updated data. If refresh fails, check the semantic model settings. If the gateway service is offline, Status is where you see the error. If Power BI can't sign in to the data sources, you see an error in Data source credentials.
On-premises data gateway
If you're using the on-premises data gateway to refresh data, you don't need to supply credentials, as they're defined for the data source by the gateway administrator.

Note
When connecting to on-premises SharePoint for data refresh, Power BI supports only Anonymous, Basic, and Windows (NTLM/Kerberos) authentication mechanisms. Power BI does not support ADFS or any Forms-Based Authentication mechanisms for data refresh of on-premises SharePoint data sources.
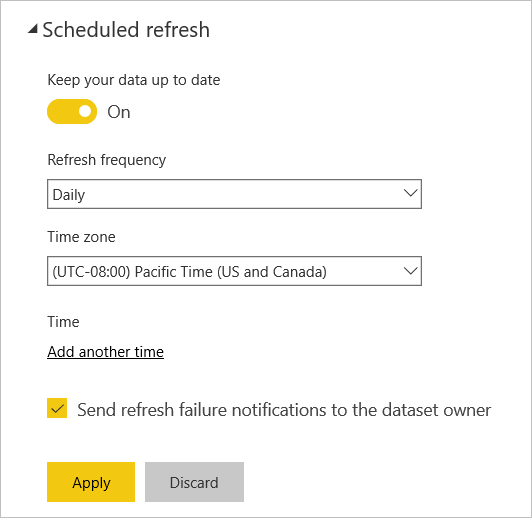
Scheduled refresh
The Refresh section is where you define the frequency and time slots to refresh the semantic model. Some data sources don't require a gateway to be configurable for refresh, while other data sources require a gateway.
In a DirectQuery scenario, when a semantic model qualifies for performance optimization, Refresh will be moved to the Optimize performance section.
Set the Configure a refresh schedule slider to On to configure the settings.
Note
The target is to initiate the refresh within 15 minutes of the scheduled time slot, but a delay of up to one hour can occur if the service can't allocate the required resources sooner. Refresh can begin as early as five minutes before the scheduled refresh time.
Note
After two months of inactivity, scheduled refresh on your semantic model is paused. A semantic model is considered inactive when no user has visited any dashboard or report built on the semantic model. When scheduled refresh is paused, the semantic model owner is sent an email. The refresh schedule for the semantic model is then displayed as disabled. To resume scheduled refresh, revisit any dashboard or report built on the semantic model.
What's supported?
Note
Power BI deactivates your refresh schedule after four consecutive failures or when the service detects an unrecoverable error that requires a configuration update, such as invalid or expired credentials. It is not possible to change the consecutive failures threshold.
Tip
Power BI does not have a monthly refresh interval option. However, you can use Power Automate to create a custom refresh interval that occurs monthly, as described in the following Power BI blog post.
Certain semantic models are supported against different gateways for scheduled refresh.
Power BI Gateway - Personal
Power BI Desktop
- All online data sources shown in Power BI Desktop's Get data and Power Query Editor.
- All on-premises data sources shown in Power BI Desktop's Get data and Power Query Editor except for Hadoop files (HDFS) and Microsoft Exchange.
Excel
- All online data sources shown in Power Query.
- All on-premises data sources shown in Power Query except for Hadoop files (HDFS) and Microsoft Exchange.
- All online data sources shown in Power Pivot.
- All on-premises data sources shown in Power Pivot except for Hadoop files (HDFS) and Microsoft Exchange.
Note
In Excel 2016 and later, Launch Power Query Editor is available from Get Data in the Data ribbon.
Power BI Gateway
For information about supported data sources, see Power BI data sources.
Troubleshooting
Sometimes refreshing data might not go as expected, typically due to an issue connected with a gateway. See these gateway troubleshooting articles for tools and known issues.
Related content
More questions? Try asking the Power BI Community