Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure AI Search can extract and index both text and images from PDF documents stored in Azure Blob Storage. This tutorial shows you how to build a multimodal indexing pipeline by describing visual content in natural language and embedding it alongside document text.
From the source document, each image is passed to the GenAI Prompt skill (preview) to generate a concise textual description. These descriptions, along with the original document text, are then embedded into vector representations using Azure OpenAI’s text-embedding-3-large model. The result is a single index containing semantically searchable content from both modalities: text and verbalized images.
In this tutorial, you use:
A 36-page PDF document that combines rich visual content, such as charts, infographics, and scanned pages, with traditional text.
The Document Extraction skill for extracting normalized images and text.
The GenAI Prompt skill (preview) to generate image captions, which are text-based descriptions of visual content, for search and grounding.
A search index configured to store text and image embeddings and support for vector-based similarity search.
This tutorial demonstrates a lower-cost approach for indexing multimodal content using Document Extraction skill and image captioning. It enables extraction and search over both text and images from documents in Azure Blob Storage. However, it doesn't include locational metadata for text, such as page numbers or bounding regions.
For a more comprehensive solution that includes structured text layout and spatial metadata, see Indexing blobs with text and images for multimodal RAG scenarios using image verbalization and Document Layout skill.
Note
Setting imageAction to generateNormalizedImages is required for this tutorial and incurs an additional charge for image extraction according to Azure AI Search pricing.
Using a REST client and the Search REST APIs you will:
- Set up sample data and configure an
azureblobdata source - Create an index with support for text and image embeddings
- Define a skillset with extraction, captioning, and embedding steps
- Create and run an indexer to process and index content
- Search the index you just created
Prerequisites
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
Azure AI Search, Basic pricing tier or higher, with a managed identity. Create a service or find an existing service in your current subscription.
Visual Studio Code with a REST client.
Download files
Download the following sample PDF:
Upload sample data to Azure Storage
In Azure Storage, create a new container named doc-extraction-image-verbalization-container.
Create a role assignment in Azure Storage and Specify a managed identity in a connection string
For connections made using a system-assigned managed identity. Provide a connection string that contains a ResourceId, with no account key or password. The ResourceId must include the subscription ID of the storage account, the resource group of the storage account, and the storage account name. The connection string is similar to the following example:
"credentials" : { "connectionString" : "ResourceId=/subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-00000000/resourceGroups/MY-DEMO-RESOURCE-GROUP/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/MY-DEMO-STORAGE-ACCOUNT/;" }For connections made using a user-assigned managed identity. Provide a connection string that contains a ResourceId, with no account key or password. The ResourceId must include the subscription ID of the storage account, the resource group of the storage account, and the storage account name. Provide an identity using the syntax shown in the following example. Set userAssignedIdentity to the user-assigned managed identity The connection string is similar to the following example:
"credentials" : { "connectionString" : "ResourceId=/subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-00000000/resourceGroups/MY-DEMO-RESOURCE-GROUP/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/MY-DEMO-STORAGE-ACCOUNT/;" }, "identity" : { "@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Azure.Search.DataUserAssignedIdentity", "userAssignedIdentity" : "/subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-00000000/resourcegroups/MY-DEMO-RESOURCE-GROUP/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/MY-DEMO-USER-MANAGED-IDENTITY" }
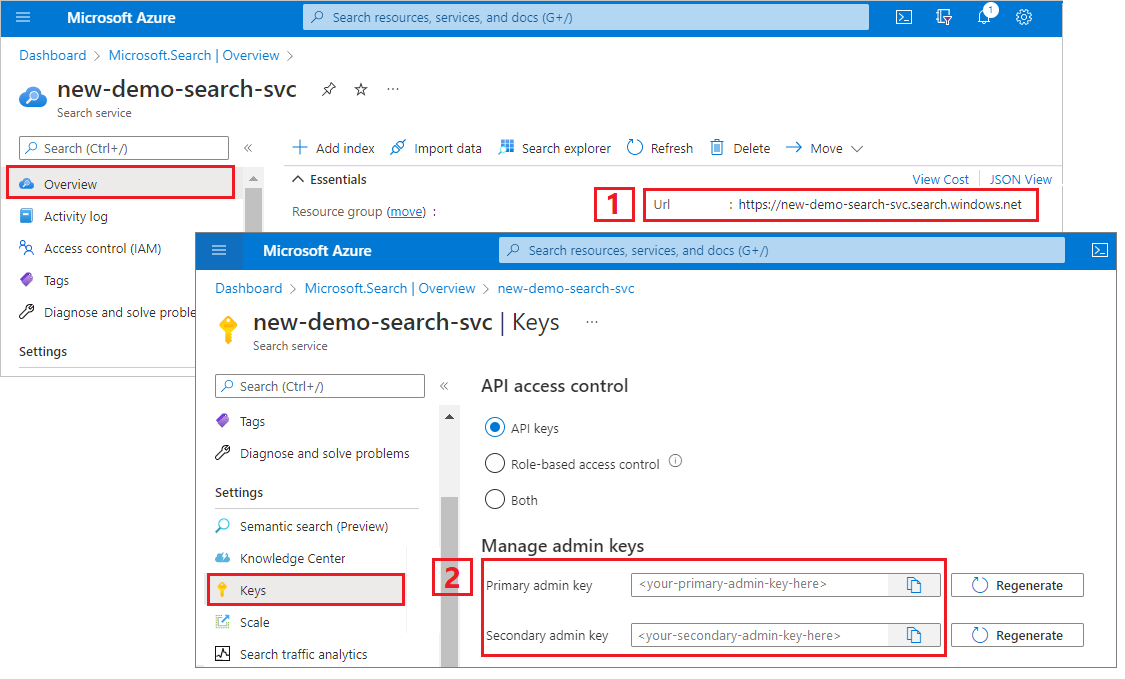
Copy a search service URL and API key
For this tutorial, connections to Azure AI Search require an endpoint and an API key. You can get these values from the Azure portal. For alternative connection methods, see Managed identities.
Sign in to the Azure portal, navigate to the search service Overview page, and copy the URL. An example endpoint might look like
https://mydemo.search.windows.net.Under Settings > Keys, copy an admin key. Admin keys are used to add, modify, and delete objects. There are two interchangeable admin keys. Copy either one.
Set up your REST file
Start Visual Studio Code and create a new file.
Provide values for variables used in the request.
@baseUrl = PUT-YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-ENDPOINT-HERE @apiKey = PUT-YOUR-ADMIN-API-KEY-HERE @storageConnection = PUT-YOUR-STORAGE-CONNECTION-STRING-HERE @openAIResourceUri = PUT-YOUR-OPENAI-URI-HERE @openAIKey = PUT-YOUR-OPENAI-KEY-HERE @chatCompletionResourceUri = PUT-YOUR-CHAT-COMPLETION-URI-HERE @chatCompletionKey = PUT-YOUR-CHAT-COMPLETION-KEY-HERE @imageProjectionContainer=PUT-YOUR-IMAGE-PROJECTION-CONTAINER-HERESave the file using a
.restor.httpfile extension.
For help with the REST client, see Quickstart: Full-text search using REST.
Create a data source
Create Data Source (REST) creates a data source connection that specifies what data to index.
### Create a data source
POST {{baseUrl}}/datasources?api-version=2025-05-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"name": "doc-extraction-image-verbalization-ds",
"description": null,
"type": "azureblob",
"subtype": null,
"credentials": {
"connectionString": "{{storageConnection}}"
},
"container": {
"name": "doc-extraction-image-verbalization-container",
"query": null
},
"dataChangeDetectionPolicy": null,
"dataDeletionDetectionPolicy": null,
"encryptionKey": null,
"identity": null
}
Send the request. The response should look like:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: application/json; odata.metadata=minimal; odata.streaming=true; charset=utf-8
Location: https://<YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-NAME>.search.windows-int.net:443/datasources('doc-extraction-image-verbalization-ds')?api-version=2025-05-01-preview -Preview
Server: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=2592000, max-age=15724800; includeSubDomains
Preference-Applied: odata.include-annotations="*"
OData-Version: 4.0
request-id: 4eb8bcc3-27b5-44af-834e-295ed078e8ed
elapsed-time: 346
Date: Sat, 26 Apr 2025 21:25:24 GMT
Connection: close
{
"name": "doc-extraction-image-verbalization-ds",
"description": "A test datasource",
"type": "azureblob",
"subtype": null,
"indexerPermissionOptions": [],
"credentials": {
"connectionString": null
},
"container": {
"name": "doc-extraction-multimodality-container",
"query": null
},
"dataChangeDetectionPolicy": null,
"dataDeletionDetectionPolicy": null,
"encryptionKey": null,
"identity": null
}
Create an index
Create Index (REST) creates a search index on your search service. An index specifies all the parameters and their attributes.
For nested JSON, the index fields must be identical to the source fields. Currently, Azure AI Search doesn't support field mappings to nested JSON, so field names and data types must match completely. The following index aligns to the JSON elements in the raw content.
### Create an index
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes?api-version=2025-05-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"name": "doc-extraction-image-verbalization-index",
"fields": [
{
"name": "content_id",
"type": "Edm.String",
"retrievable": true,
"key": true,
"analyzer": "keyword"
},
{
"name": "text_document_id",
"type": "Edm.String",
"searchable": false,
"filterable": true,
"retrievable": true,
"stored": true,
"sortable": false,
"facetable": false
},
{
"name": "document_title",
"type": "Edm.String",
"searchable": true
},
{
"name": "image_document_id",
"type": "Edm.String",
"filterable": true,
"retrievable": true
},
{
"name": "content_text",
"type": "Edm.String",
"searchable": true,
"retrievable": true
},
{
"name": "content_embedding",
"type": "Collection(Edm.Single)",
"dimensions": 3072,
"searchable": true,
"retrievable": true,
"vectorSearchProfile": "hnsw"
},
{
"name": "content_path",
"type": "Edm.String",
"searchable": false,
"retrievable": true
},
{
"name": "offset",
"type": "Edm.String",
"searchable": false,
"retrievable": true
},
{
"name": "location_metadata",
"type": "Edm.ComplexType",
"fields": [
{
"name": "page_number",
"type": "Edm.Int32",
"searchable": false,
"retrievable": true
},
{
"name": "bounding_polygons",
"type": "Edm.String",
"searchable": false,
"retrievable": true,
"filterable": false,
"sortable": false,
"facetable": false
}
]
}
],
"vectorSearch": {
"profiles": [
{
"name": "hnsw",
"algorithm": "defaulthnsw",
"vectorizer": "{{vectorizer}}"
}
],
"algorithms": [
{
"name": "defaulthnsw",
"kind": "hnsw",
"hnswParameters": {
"m": 4,
"efConstruction": 400,
"metric": "cosine"
}
}
],
"vectorizers": [
{
"name": "{{vectorizer}}",
"kind": "azureOpenAI",
"azureOpenAIParameters": {
"resourceUri": "{{openAIResourceUri}}",
"deploymentId": "text-embedding-3-large",
"apiKey": "{{openAIKey}}",
"modelName": "text-embedding-3-large"
}
}
]
},
"semantic": {
"defaultConfiguration": "semanticconfig",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "semanticconfig",
"prioritizedFields": {
"titleField": {
"fieldName": "document_title"
},
"prioritizedContentFields": [
],
"prioritizedKeywordsFields": []
}
}
]
}
}
Key points:
Text and image embeddings are stored in the
content_embeddingfield and must be configured with appropriate dimensions (for example, 3072) and a vector search profile.location_metadatacaptures bounding polygon and page number metadata for each normalized image, enabling precise spatial search or UI overlays.location_metadataonly exists for images in this scenario. If you'd like to capture locational metadata for text as well, consider using Document Layout skill. An in-depth tutorial is linked at the bottom of the page.For more information on vector search, see Vectors in Azure AI Search.
For more information on semantic ranking, see Semantic ranking in Azure AI Search
Create a skillset
Create Skillset (REST) creates a search index on your search service. An index specifies all the parameters and their attributes.
### Create a skillset
POST {{baseUrl}}/skillsets?api-version=2025-05-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"name": "doc-extraction-image-verbalization-skillset",
"description": "A test skillset",
"skills": [
{
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Skills.Util.DocumentExtractionSkill",
"name": "document-extraction-skill",
"description": "Document extraction skill to exract text and images from documents",
"parsingMode": "default",
"dataToExtract": "contentAndMetadata",
"configuration": {
"imageAction": "generateNormalizedImages",
"normalizedImageMaxWidth": 2000,
"normalizedImageMaxHeight": 2000
},
"context": "/document",
"inputs": [
{
"name": "file_data",
"source": "/document/file_data"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"name": "content",
"targetName": "extracted_content"
},
{
"name": "normalized_images",
"targetName": "normalized_images"
}
]
},
{
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Skills.Text.SplitSkill",
"name": "split-skill",
"description": "Split skill to chunk documents",
"context": "/document",
"defaultLanguageCode": "en",
"textSplitMode": "pages",
"maximumPageLength": 2000,
"pageOverlapLength": 200,
"unit": "characters",
"inputs": [
{
"name": "text",
"source": "/document/extracted_content",
"inputs": []
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"name": "textItems",
"targetName": "pages"
}
]
},
{
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Skills.Text.AzureOpenAIEmbeddingSkill",
"name": "text-embedding-skill",
"description": "Embedding skill for text",
"context": "/document/pages/*",
"inputs": [
{
"name": "text",
"source": "/document/pages/*"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"name": "embedding",
"targetName": "text_vector"
}
],
"resourceUri": "{{openAIResourceUri}}",
"deploymentId": "text-embedding-3-large",
"apiKey": "{{openAIKey}}",
"dimensions": 3072,
"modelName": "text-embedding-3-large"
},
{
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Skills.Custom.ChatCompletionSkill",
"name": "genAI-prompt-skill",
"description": "GenAI Prompt skill for image verbalization",
"uri": "{{chatCompletionResourceUri}}",
"timeout": "PT1M",
"apiKey": "{{chatCompletionKey}}",
"context": "/document/normalized_images/*",
"inputs": [
{
"name": "systemMessage",
"source": "='You are tasked with generating concise, accurate descriptions of images, figures, diagrams, or charts in documents. The goal is to capture the key information and meaning conveyed by the image without including extraneous details like style, colors, visual aesthetics, or size.\n\nInstructions:\nContent Focus: Describe the core content and relationships depicted in the image.\n\nFor diagrams, specify the main elements and how they are connected or interact.\nFor charts, highlight key data points, trends, comparisons, or conclusions.\nFor figures or technical illustrations, identify the components and their significance.\nClarity & Precision: Use concise language to ensure clarity and technical accuracy. Avoid subjective or interpretive statements.\n\nAvoid Visual Descriptors: Exclude details about:\n\nColors, shading, and visual styles.\nImage size, layout, or decorative elements.\nFonts, borders, and stylistic embellishments.\nContext: If relevant, relate the image to the broader content of the technical document or the topic it supports.\n\nExample Descriptions:\nDiagram: \"A flowchart showing the four stages of a machine learning pipeline: data collection, preprocessing, model training, and evaluation, with arrows indicating the sequential flow of tasks.\"\n\nChart: \"A bar chart comparing the performance of four algorithms on three datasets, showing that Algorithm A consistently outperforms the others on Dataset 1.\"\n\nFigure: \"A labeled diagram illustrating the components of a transformer model, including the encoder, decoder, self-attention mechanism, and feedforward layers.\"'"
},
{
"name": "userMessage",
"source": "='Please describe this image.'"
},
{
"name": "image",
"source": "/document/normalized_images/*/data"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"name": "response",
"targetName": "verbalizedImage"
}
]
},
{
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Skills.Text.AzureOpenAIEmbeddingSkill",
"name": "verblized-image-embedding-skill",
"description": "Embedding skill for verbalized images",
"context": "/document/normalized_images/*",
"inputs": [
{
"name": "text",
"source": "/document/normalized_images/*/verbalizedImage",
"inputs": []
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"name": "embedding",
"targetName": "verbalizedImage_vector"
}
],
"resourceUri": "{{openAIResourceUri}}",
"deploymentId": "text-embedding-3-large",
"apiKey": "{{openAIKey}}",
"dimensions": 3072,
"modelName": "text-embedding-3-large"
},
{
"@odata.type": "#Microsoft.Skills.Util.ShaperSkill",
"name": "shaper-skill",
"description": "Shaper skill to reshape the data to fit the index schema"
"context": "/document/normalized_images/*",
"inputs": [
{
"name": "normalized_images",
"source": "/document/normalized_images/*",
"inputs": []
},
{
"name": "imagePath",
"source": "='{{imageProjectionContainer}}/'+$(/document/normalized_images/*/imagePath)",
"inputs": []
},
{
"name": "location_metadata",
"sourceContext": "/document/normalized_images/*",
"inputs": [
{
"name": "page_number",
"source": "/document/normalized_images/*/pageNumber"
},
{
"name": "bounding_polygons",
"source": "/document/normalized_images/*/boundingPolygon"
}
]
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"name": "output",
"targetName": "new_normalized_images"
}
]
}
],
"indexProjections": {
"selectors": [
{
"targetIndexName": "{{index}}",
"parentKeyFieldName": "text_document_id",
"sourceContext": "/document/pages/*",
"mappings": [
{
"name": "content_embedding",
"source": "/document/pages/*/text_vector"
},
{
"name": "content_text",
"source": "/document/pages/*"
},
{
"name": "document_title",
"source": "/document/document_title"
}
]
},
{
"targetIndexName": "{{index}}",
"parentKeyFieldName": "image_document_id",
"sourceContext": "/document/normalized_images/*",
"mappings": [
{
"name": "content_text",
"source": "/document/normalized_images/*/verbalizedImage"
},
{
"name": "content_embedding",
"source": "/document/normalized_images/*/verbalizedImage_vector"
},
{
"name": "content_path",
"source": "/document/normalized_images/*/new_normalized_images/imagePath"
},
{
"name": "document_title",
"source": "/document/document_title"
},
{
"name": "locationMetadata",
"source": "/document/normalized_images/*/new_normalized_images/location_metadata"
}
]
}
],
"parameters": {
"projectionMode": "skipIndexingParentDocuments"
}
},
"knowledgeStore": {
"storageConnectionString": "{{storageConnection}}",
"projections": [
{
"files": [
{
"storageContainer": "{{imageProjectionContainer}}",
"source": "/document/normalized_images/*"
}
]
}
]
}
}
This skillset extracts text and images, vectorizes both, and shapes the image metadata for projection into the index.
Key points:
The
content_textfield is populated in two ways:From document text extracted using the Document Extraction skill and chunked using the Text Split skill
From image content using the GenAI Prompt skill, which generates descriptive captions for each normalized image
The
content_embeddingfield contains 3072-dimensional embeddings for both page text and verbalized image descriptions. These are generated using the text-embedding-3-large model from Azure OpenAI.content_pathcontains the relative path to the image file within the designated image projection container. This field is generated only for images extracted from PDFs whenimageActionis set togenerateNormalizedImages, and can be mapped from the enriched document from the source field/document/normalized_images/*/imagePath.
Create and run an indexer
Create Indexer creates an indexer on your search service. An indexer connects to the data source, loads data, runs a skillset, and indexes the enriched data.
### Create and run an indexer
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexers?api-version=2025-05-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"dataSourceName": "doc-extraction-image-verbalization-ds",
"targetIndexName": "doc-extraction-image-verbalization-index",
"skillsetName": "doc-extraction-image-verbalization-skillset",
"parameters": {
"maxFailedItems": -1,
"maxFailedItemsPerBatch": 0,
"batchSize": 1,
"configuration": {
"allowSkillsetToReadFileData": true
}
},
"fieldMappings": [
{
"sourceFieldName": "metadata_storage_name",
"targetFieldName": "document_title"
}
],
"outputFieldMappings": []
}
Run queries
You can start searching as soon as the first document is loaded.
### Query the index
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes/doc-extraction-image-verbalization-index/docs/search?api-version=2025-05-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"search": "*",
"count": true
}
Send the request. This is an unspecified full-text search query that returns all of the fields marked as retrievable in the index, along with a document count. The response should look like:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: application/json; odata.metadata=minimal; odata.streaming=true; charset=utf-8
Content-Encoding: gzip
Vary: Accept-Encoding
Server: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=2592000, max-age=15724800; includeSubDomains
Preference-Applied: odata.include-annotations="*"
OData-Version: 4.0
request-id: 712ca003-9493-40f8-a15e-cf719734a805
elapsed-time: 198
Date: Wed, 30 Apr 2025 23:20:53 GMT
Connection: close
{
"@odata.count": 100,
"@search.nextPageParameters": {
"search": "*",
"count": true,
"skip": 50
},
"value": [
],
"@odata.nextLink": "https://<YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-NAME>.search.windows.net/indexes/doc-extraction-image-verbalization-index/docs/search?api-version=2025-05-01-preview "
}
100 documents are returned in the response.
For filters, you can also use Logical operators (and, or, not) and comparison operators (eq, ne, gt, lt, ge, le). String comparisons are case -sensitive. For more information and examples, see Examples of simple search queries.
Note
The $filter parameter only works on fields that were marked filterable during index creation.
Here are some examples of other queries:
### Query for only images
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes/doc-extraction-image-verbalization-index/docs/search?api-version=2025-05-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"search": "*",
"count": true,
"filter": "image_document_id ne null"
}
### Query for text or images with content related to energy, returning the id, parent document, and text (extracted text for text chunks and verbalized image text for images), and the content path where the image is saved in the knowledge store (only populated for images)
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes/doc-extraction-image-verbalization-index/docs/search?api-version=2025-05-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"search": "energy",
"count": true,
"select": "content_id, document_title, content_text, content_path"
}
Reset and rerun
Indexers can be reset to clear the high-water mark, which allows a full rerun. The following POST requests are for reset, followed by rerun.
### Reset the indexer
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexers/doc-extraction-image-verbalization-indexer/reset?api-version=2025-05-01-preview HTTP/1.1
api-key: {{apiKey}}
### Run the indexer
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexers/doc-extraction-image-verbalization-indexer/run?api-version=2025-05-01-preview HTTP/1.1
api-key: {{apiKey}}
### Check indexer status
GET {{baseUrl}}/indexers/doc-extraction-image-verbalization-indexer/status?api-version=2025-05-01-preview HTTP/1.1
api-key: {{apiKey}}
Clean up resources
When you're working in your own subscription, at the end of a project, it's a good idea to remove the resources that you no longer need. Resources left running can cost you money. You can delete resources individually or delete the resource group to delete the entire set of resources.
You can use the Azure portal to delete indexes, indexers, and data sources.
See also
Now that you're familiar with a sample implementation of a multimodal indexing scenario, check out: