Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
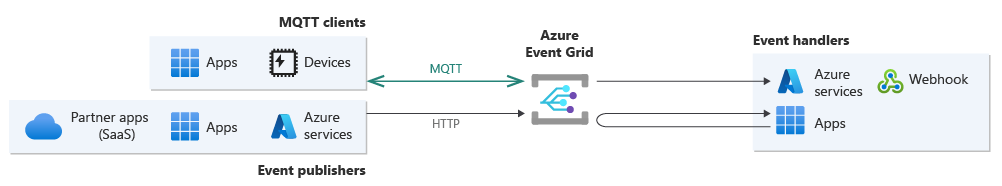
Azure Event Grid is a highly scalable and fully managed publish-subscribe service for message distribution. Event Grid offers flexible message consumption patterns and uses the Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) and HTTP protocols. With Event Grid, you can build data pipelines with device data, integrate applications, and build event-driven serverless architectures.
Event Grid enables clients to publish and subscribe to messages over the MQTT v3.1.1 and v5.0 protocols to support Internet of Things (IoT) solutions. Through HTTP, you can use Event Grid to build event-driven solutions where a publisher service announces its system state changes (events) to subscriber applications. You can configure Event Grid to send events to subscribers (push delivery), or subscribers can connect to Event Grid to read events (pull delivery). Event Grid supports the CloudEvents 1.0 specification to provide interoperability across systems.
Core features
Event Grid has two main features:
MQTT messaging: IoT devices and applications can communicate with each other over MQTT. You can also use Event Grid to route MQTT messages to Azure services or custom endpoints for further data analysis, visualization, or storage. By using this integration with Azure services, you can build data pipelines that start with data ingestion from your IoT devices.
Data distribution by using push and pull delivery modes: At any point in a data pipeline, HTTP applications can consume messages by using push or pull APIs. The source of the data might include MQTT clients' data, but it also includes the following data sources that send their events over HTTP:
- Azure services
- Your custom applications
- External partner (software as a service) systems
The Event Grid push delivery mechanism sends data to destinations that include your own application webhooks and Azure services. Here's a look at these two features.
MQTT messaging
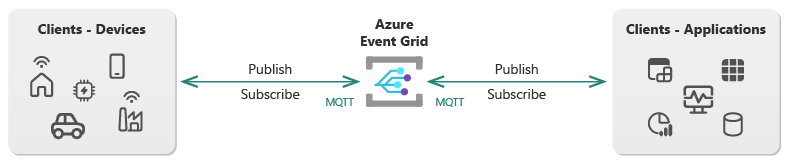
Event Grid enables your clients to communicate on custom MQTT topic names by using a publish-subscribe messaging model. Event Grid supports clients that publish and subscribe to messages over MQTT v3.1.1, MQTT v3.1.1 over WebSocket, MQTT v5, and MQTT v5 over WebSocket.
Event Grid also supports devices and services that send MQTT messages over HTTPS, which simplifies integration with non-MQTT clients. Event Grid allows you to send MQTT messages to the cloud for data analysis, storage, and visualizations, among other use cases. This feature is currently in preview.
Event Grid integrates with Azure IoT Operations to bridge its MQTT broker capability on the edge with the Event Grid MQTT broker capability in the cloud. Azure IoT MQTT broker is a new distributed MQTT broker for edge computing that runs on Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters. It's now available as part of Azure IoT Operations.
The MQTT broker feature in Event Grid is ideal for the automotive, mobility, and manufacturing scenarios, among others. To learn how to build secure and scalable solutions to connect millions of MQTT clients to the cloud by using Azure messaging and data analytics services, see the automotive and manufacturing reference architectures.
Highlights of MQTT messaging support in Event Grid:
- MQTT v3.1.1 and MQTT v5.0 support: Uses any open-source MQTT client library to communicate with the service.
- Custom topics with wildcard support: Uses your own topic structure.
- Publish-subscribe messaging model: Communicates efficiently by using one-to-many, many-to-one, and one-to-one messaging patterns.
- Built-in cloud integration: Routes your MQTT messages to Azure services or custom webhooks for further processing.
- Flexible and fine-grained access control model: Groups clients and topics to simplify access control management. Uses the variable support in topic templates for fine-grained access control.
- MQTT broker authentication methods: Uses X.509 certificate authentication, an industry authentication standard for IoT devices. Uses Microsoft Entra ID authentication, an Azure authentication standard for applications. Uses flexible authentication patterns like OAuth 2.0 JSON Web Token (JWT) authentication, which is lightweight and secure for MQTT clients that aren't provisioned in Azure. Uses custom webhook authentication, which allows external HTTP endpoints (webhooks) to authenticate MQTT connections dynamically. This method uses Entra ID JWT validation to ensure secure access.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.2 and TLS 1.3 support: Secures your client communication by using robust encryption protocols.
- Multi-session support: Connects your applications with multiple active sessions to ensure reliability and scalability.
- MQTT over WebSocket: Enables connectivity for clients in firewall-restricted environments.
- Custom domain names: Allows users to assign their own domain names to an Event Grid namespace's MQTT endpoints, which enhances security and simplifies client configuration.
- Client life-cycle events: Allows applications to react to events about the client connection status or the client resource operations.
- HTTP Publish: Enables devices and services to send MQTT messages to Event Grid over HTTPS, which simplifies integration with non-MQTT clients.
- MQTT Retain: Ensures that the last known message on a topic is automatically delivered to new subscribers, which enables instant state synchronization.
For more information about the MQTT broker, see the following articles:
- Overview
- Publish and subscribe to MQTT messages
- Tutorial: Route MQTT messages to Azure Event Hubs by using namespace topics
- Tutorial: Route MQTT messages to Azure Functions by using custom topics
Event messaging (HTTP)
Event Grid supports push and pull event delivery by using HTTP. With push delivery, you define a destination in an event subscription, to which Event Grid sends events. With pull delivery, subscriber applications connect to Event Grid to consume events. Pull delivery is supported for topics in an Event Grid namespace.
Event handlers
In the push delivery, an event subscription is a generic configuration resource that you can use to define the event handler or destination to which events are sent by using push delivery. For example, you can send data to a webhook, an Azure function, or event hubs. For a complete list of event handlers that are supported, see:
- Event handlers supported on namespace topics.
- Event handlers supported on custom, system, domain, and partner topics.
Push delivery vs. pull delivery
The following general guidelines help you decide when to use pull or push delivery.
Pull delivery
- You need full control over when to receive events. For example, your application might not be up all the time or not stable enough. You might also process data only at certain times.
- You need full control over event consumption. For example, a downstream service or layer in your consumer application might have a problem that prevents you from processing events. In that case, the pull delivery API allows the consumer app to release an already read event back to the broker for delivery later.
- You want to use private links when you receive events, which is possible only with the pull delivery, not the push delivery.
- You don't have the ability to expose an endpoint and use push delivery, but you can connect to Event Grid to consume events.
Push delivery
- You want to avoid constant polling to determine that a system state change occurred. Instead, you want to use Event Grid to send events to you when state changes happen.
- You have an application that can't make outbound calls. For example, your organization might be concerned about data exfiltration. However, your application can receive events through a public endpoint.
HTTP model highlights:
- Flexible event consumption model: Consume events by using pull or push delivery mode when you use HTTP.
- System events: Get up and running quickly with built-in Azure service events.
- Your own application events: Use Event Grid to route, filter, and reliably deliver custom events from your app.
- Partner events: Subscribe to your partner SaaS provider events and process them on Azure.
- Advanced filtering: Filter on event type or other event attributes to make sure your event handlers or consumer apps receive only relevant events.
- Reliability: Push delivery features a 24-hour retry mechanism with exponential backoff to make sure that events are delivered. If you use pull delivery, your application has full control over event consumption.
- High throughput: Build high-volume integrated solutions with Event Grid.
- Custom domain names: Allow users to assign their own domain names to an Event Grid namespace's HTTP endpoints, which enhances security and simplifies client configuration.
For more information, see the following articles:
- Pull delivery overview
- Push delivery overview
- Concepts
- Quickstart: Publish and subscribe to app events by using namespace topics
Use cases
For a list of use cases where you can use Event Grid, see Use cases.
Supported regions
The new MQTT broker and namespace topics features are available in the following regions.
| Region | Region | Region | Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia East | Australia South East | Australia Central | Australia Central 2 |
| Brazil South | Brazil Southeast | Canada Central | Canada East |
| Central India | Central US | East Asia | East US |
| East US 2 | West US | France Central | France South |
| Germany North | Germany West Central | Israel Central | Italy North |
| Japan East | Japan West | Korea Central | Korea South |
| Mexico Central | North Central US | North Europe | Norway East |
| Poland Central | South Africa West | South Africa North | South Central US |
| South India | Southeast Asia | Spain Central | Sweden Central |
| Sweden South | Switzerland North | Switzerland West | UAE North |
| UAE Central | UK South | UK West | West Europe |
| West US 2 | West US 3 | West Central US |