Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how to enable and integrate software defined networking (SDN) on your existing Azure Local instance. You use a PowerShell action plan to enable SDN.
Important
This feature is currently in PREVIEW. See the Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews for legal terms that apply to Azure features that are in beta, preview, or otherwise not yet released into general availability.
About SDN integration in Azure Local
For SDN enabled by Arc, the Network Controller (NC) is deployed as a Failover Cluster service managed by the orchestrator (also known as Lifecycle Manager). You run an orchestrator command that integrates the NC into the Azure Local platform.
Once the NC is integrated, SDN is enabled. You can use the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure Resource Manager templates to create and manage the following SDN features:
Logical networks: You can create SDN static logical networks that project your physical networks. For more information, see Create logical networks.
Network interfaces: You can create and attach network interfaces to virtual machines and assign them IP addresses from the logical network. For more information, see Create network interfaces.
Network Security Group (NSG): You can create and apply NSGs to network interfaces or logical networks to filter network traffic. You can also create default network access policies and network security rules to allow or deny traffic to and from network interfaces and logical networks.
For more information, see Create network security groups and see Create network security rules.
About Network Controller architecture on Azure Local
NC is a key component that manages and configures virtual network infrastructure on an Azure Local instance. NC is now natively integrated with the host machine using Failover Clustering, rather than being hosted in a VM. NC is responsible for managing the virtual switch, logical networks, and network interfaces. It also provides a REST API for programmatic access to the network infrastructure.
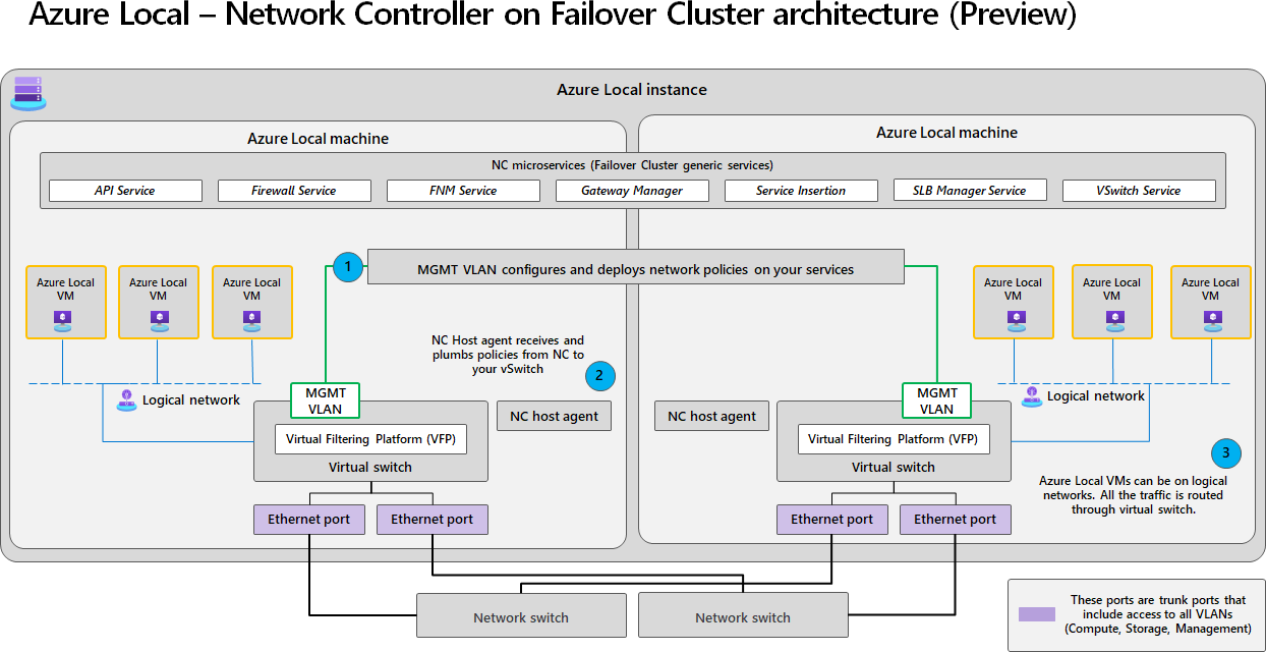
Here's an architecture diagram of Network Controller in a 2-node Azure Local instance with SDN enabled by Arc:
In this example, the network topology includes two Azure Local machines clustered together with two Top-of-Rack (ToR) switches. The Network Controller component and its services are set as a Failover Cluster group across all the Azure Local machines in your instance. Each Network Controller microservice is highly available as a Failover Cluster Resource Group.
- MGMT VLAN on your Azure Local instance is responsible for configuring and deploying network policies from NC to NC host agent.
- NC host agent receives and plumbs policies to your virtual switch.
- Tenant VMs reside on logical networks managed by NC. All the traffic from these VMs is routed through the virtual switches that are Virtual Filtering Platform (VFP)-enabled.
Considerations for SDN enabled by Arc
Important
- SDN enabled by Arc is a preview feature. Once you enable SDN, you can't roll back or disable.
- If you are already running Network controller on your Azure Local cluster that was deployed using on-premises tools, you must not attempt to run this method.
- The only VMs that are in scope for using NSGs with this feature are Azure Local VMs. These are the VMs that were deployed from Azure client interfaces (Azure CLI, Azure portal, Azure Resource Manager). Do not use an Azure Local VM in conjunction with an NSG that is managed and applied from on-premises tools.
For your existing Azure Local instances:
- Enabling SDN with existing Azure Local VMs and logical networks is supported.
- The logical networks and network interfaces are automatically hydrated into the Network Controller.
- Make sure to plan for a maintenance window if you're running on a production environment. Your workloads experience a short network disruption while SDN Azure Virtual Filtering Platform policies are applied.
Prerequisites
You have access to an Azure Local instance running 2506 and later. The OS build must be 26100.xxxx or later. Check the OS version via Azure portal or via the PowerShell:
In the Azure portal, go to your Azure Local instance and select Overview. The OS version is displayed in the Instance details section.
Connect to a machine on your Azure Local instance and run the following PowerShell command to verify the OS version:
systeminfo.exeHere's an example output:
[v-host1]: PS C:\DeploymentUser> systeminfo.exe Host Name: V-HOST1 OS Name: Microsoft Azure Stack HCI OS Version: 10.0.26100 N/A Build 26100 OS Manufacturer: Microsoft Corporation OS Configuration: Member Server OS Build Type: Multiprocessor Free ====SNIPPED========SNIPPED========SNIPPED========SNIPPED==== Security Features Enabled: Hyper-V Requirements: A hypervisor has been detected. Features required for Hyper-V will not be displayed.- Verify that the
OS Versionin the output is 10.0.26100.
- Verify that the
You have access to a node of your Azure Local instance with the Azure Stack HCI administrator role. This role is required to run the cmdlet.
You have access to a client used to connect to Azure Local instance.
You have access to an Azure subscription with the Azure Stack HCI Administrator role-based access control (RBAC) role. This role grants full access to your Azure Local instance and its resources.
An Azure Stack HCI administrator can register the Azure Local instance and assign Azure Stack HCI VM contributor and Azure Stack HCI VM reader roles to other users. For more information, see Use Role-based Access Control to manage Azure Local VMs enabled by Azure Arc.
Choose an SDN prefix
When you enable SDN, you will be required to provide an SDN prefix. Make sure that the SDN prefix meets the following requirements:
- Must not be null or empty.
- Must be eight or fewer characters.
- Must contain only lowercase, uppercase, numeric, characters.
- Can contain hyphens but must not contain two consecutive hyphens or end with a hyphen.
If the prefix doesn't meet these requirements, the SDN enablement fails.
Prepare the DNS environment
Prepare your DNS environment before you enable SDN. The SDN integration requires A DNS record for the Network Controller REST URL, which is used to access the Network Controller REST API.
Static DNS environment: Precreate the DNS record for the Network Controller REST URL. For more information, see Precreate a DNS record.
- The name for your DNS record is derived from your SDN prefix. The A DNS record must be
<SDNPrefix>-NC. - The DNS record must resolve to the reserved IP.
- Assign the 5th IP address in the IP address range to the A DNS record. You provided this IP ranged when configuring the Network settings during the deployment of your Azure Local instance.
- The link shouldn't resolve to an existing DNS record.
- The name for your DNS record is derived from your SDN prefix. The A DNS record must be
Dynamic DNS environment: If you have an Active Directory integrated dynamic DNS environment, no action is required on your part. The action plan automatically creates A DNS record.
If updates are not enabled for your Dynamic DNS environment, you can choose to enable dynamic DNS updates for the DNS zone where the Network Controller REST URL is registered.
- On the DNS server, open the DNS Manager console.
- In the left pane, select Forward Lookup Zones.
- Right-click the zone that hosts the Network Controller name record, then select Properties.
- On the General tab, next to Dynamic updates, select Secure only.
For more information, see Enable dynamic DNS updates in a DNS zone.
Review cmdlet parameters
The SDN enablement cmdlet uses the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Pass the name as NC. No other user input is allowed. |
| SDNPrefix | This parameter is used for Network Controller REST URL to differentiate network controllers across Azure Local instances. For example, <SDNPrefix> makes https://<SDNPrefix>-NC.domainname/ as the NC REST URL for the Azure Local instance. Make sure that the SDN prefix meets the requirements included in Choose an SDN prefix. |
Run the cmdlet to enable SDN
Important
Make sure to plan for a maintenance window if you're running on a production environment.
Follow these steps to enable SDN on your Azure Local instance:
Verify that you're Connected to a node of your Azure Local instance with Azure Stack HCI administrator role.
Run the cmdlet to deploy Network Controller as a Failover Cluster Service. Open a PowerShell command prompt and run the following command.
#Run the LCM action plan to install Network Controller as Failover Cluster Service. Replace <SDNPrefix> with your SDN prefix. Add-EceFeature -Name NC -SDNPrefix <SDNPrefix>Confirm when prompted to proceed.
Tip
To skip the confirmation prompt, use the
-AcknowledgeMaintenanceWindowparameter.This step can take up to 20 minutes.
Validate that Network Controller is successfully added to your instance. Once the Network Controller is added, the
Add-EceFeaturecommand shows the action plan outcome.Expand this section to see an example output.
VERBOSE: Adding ECE feature NC; transcript started at C:\MASLogs\Add-EceFeature.2025-04-17.20-52-14 Disclaimer: Network Controller installation will cause network connectivity interruptions. Before proceeding with the NC enablement operation, please ensure a maintenance window is properly arranged for running on a production environment. Proceeding? [Yes/NO] : Yes Start End Duration Type Status Name ----- --- -------- ---- ------ ---- 03/11/2025 10:29:52 PM 03/11/2025 10:31:13 PM 00.00:01:20 Action Success └─(A)CleanNCSecret 03/11/2025 10:29:52 PM 03/11/2025 10:31:13 PM 00.00:01:20 Step Success └─(S)1 Parallel per-node operation top step ==========SNIPPED======SNIPPED==========SNIPPED=========SNIPPED======== 03/11/2025 10:29:52 PM 03/11/2025 10:31:12 PM 00.00:01:20 Step Success └─(S)1.1 Clean up NC secrets 03/11/2025 10:29:52 PM 03/11/2025 10:31:12 PM 00.00:01:20 Task Success └─(T)[RemoteNode=Machine2>] Role=Cloud\Fabric\NC Interface=CleanNCRestSecret InstanceID : <Instance1 ID> ActionTypeName : CleanNCSecret Status : Completed StartDateTime : 3/11/2025 10:29:51 PM EndDateTime : 3/11/2025 10:31:18 PM Start End Duration Type Status Name ----- --- -------- ---- ------ ---- 03/11/2025 10:31:52 PM 03/11/2025 10:31:57 PM 00.00:00:04 Action Success └─(A)GenerateCertificates 03/11/2025 10:31:52 PM 03/11/2025 10:31:57 PM 00.00:00:04 Step Success └─(S)1 Generate NC Rest certificate 03/11/2025 10:31:52 PM 03/11/2025 10:31:57 PM 00.00:00:04 Task Success └─(T)Role=Cloud\Infrastructure\ASCA Interface=GenerateSSLCertificatesForNCDeployment InstanceID : <Instance2 ID> ActionTypeName : GenerateCertificates Status : Completed StartDateTime : 3/11/2025 10:31:52 PM EndDateTime : 3/11/2025 10:32:02 PM Start End Duration Type Status Name ----- --- -------- ---- ------ ---- 03/11/2025 10:32:53 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:50 PM 00.00:08:57 Action Success └─(A)EnableMOCSDN 03/11/2025 10:32:53 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:50 PM 00.00:08:57 Step Success └─(S)1 FCNC deployment and MOC hydration. 03/11/2025 10:32:53 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:50 PM 00.00:08:57 Task Success └─(T)Role=Cloud\Fabric\NC Action=DeployFCNCHydrateMOC ======SNIPPED=========SNIPPED============SNIPPED ==========SNIPPED======== 03/11/2025 10:40:19 PM 03/11/2025 10:40:25 PM 00.00:00:06 Step Success │ │ ├─(S)1 Check Firewall Rules 03/11/2025 10:40:19 PM 03/11/2025 10:40:25 PM 00.00:00:06 Task Success │ │ │ └─(T)Role=Cloud\Fabric\NC Interface=VerifyNCFirewallRulesEnabled 03/11/2025 10:40:25 PM 03/11/2025 10:40:32 PM 00.00:00:06 Step Success │ │ └─(S)2 Check VM switch extension is enabled 03/11/2025 10:40:25 PM 03/11/2025 10:40:32 PM 00.00:00:06 Task Success │ │ └─(T)Role=Cloud\Fabric\NC Interface=VerifyNCVMSwitchExtensionEnabled 03/11/2025 10:41:13 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:21 PM 00.00:00:07 Step Success │ └─(S)1.1.0.9.2 VerifyNCResources 03/11/2025 10:41:13 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:21 PM 00.00:00:07 Task Success │ └─(T)Role=Cloud\Fabric\NC Interface=VerifyNCResources 03/11/2025 10:41:21 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:50 PM 00.00:00:29 Step Success └─(S)1.2 Enable FCNC SDN for MOC 03/11/2025 10:41:21 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:50 PM 00.00:00:29 Task Success └─(T)Role=Cloud\Fabric\NC Action=SetMOCSDNEnabled 03/11/2025 10:41:21 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:50 PM 00.00:00:29 Action Success └─(A)SetMOCSDNEnabled 03/11/2025 10:41:21 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:43 PM 00.00:00:22 Step Success ├─(S)1.2.1 Enable FCNC SDN for MOC 03/11/2025 10:41:21 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:43 PM 00.00:00:22 Task Success │ └─(T)Role=Cloud\Fabric\NC Interface=EnableSDNForMOC 03/11/2025 10:41:43 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:50 PM 00.00:00:07 Step Success └─(S)1.2.2 Flag FCNC deployed 03/11/2025 10:41:43 PM 03/11/2025 10:41:50 PM 00.00:00:07 Task Success └─(T)Role=Cloud\Fabric\NC Interface=SetFCNCCompleteMOCHydrated InstanceID : <Instance ID> ActionTypeName : EnableMOCSDN Status : Completed StartDateTime : 3/11/2025 10:32:52 PM EndDateTime : 3/11/2025 10:41:55 PM VERBOSE: Full XML progress log file located at: C:\MASLogs\EnableMOCSDN.2025-03-11.22-32-52 WARNING: Unable to find volume with label Deployment VERBOSE: SDN Network Controller URL is https://v-NC.domainname/ VERBOSE: Enabling SDN for MOC completed. 0 VERBOSE: Transcript stopped at C:\MASLogs\Add-EceFeature.2025-03-11.22-29-49
Next steps
This feature is available only in Azure Local 2506 or later.